Introduction to Fundamental Analysis

Fundamental analysis is a way to predict future market prices by studying various macroeconomic indicators and the activities of central banks. It helps reveal price trends and movements even without using technical tools like indicators or price patterns. It should be mentioned that fundamental analysis is far more complex than technical analysis, which is one of the reasons why the majority of traders prefer the latter, as it requires no knowledge of economics at all.
The main idea of fundamental analysis is to predict the behavior of market participants based on their perception of the current price and the macroeconomic/financial environment. Therefore, before even describing those indicators and events that may impact price fluctuations, we are going to provide you with the supply and demand basics. Use this knowledge to start trading at Binolla.
Contents
- 1 Supply and Demand Concept
- 2 Fundamental Analysis indicators
- 3 Fundamental Analysis vs. News Trading: What is the Difference Between Them?
- 4 Try trading with Fundamentals on the Binolla platform!
- 5 Central Banks Decisions: How They Affect Forex Currencies
- 6 Fundamental Analysis: How It Works
- 7 Fundamental Analysis and Market Expectations
- 8 What Should I Know to Use Fundamental Analysis
- 9 Example of Using Fundamental Analysis
- 10 Key Differences Between Fundamental Analysis
- 11 Fundamental Analysis Pros and Cons
- 12 Fundamental or Technical Analysis: What Is Better?
- 13 Conclusion
- 14 FAQ
Supply and Demand Concept
Similar to any other market, Forex currencies, stocks, commodities, and even cryptocurrencies are driven by supply and demand. The relationship between them influences market prices. When demand goes up, the price of the product rises, while when supply is higher than demand, the product’s price plunges. To better understand this concept, let’s take a look at a simple example.
Imagine that it was a good year for apple farmers. The inventories are overcrowded with this fruit. However, buyers are not ready to purchase more than they need. In this particular situation, retailers will have to reduce prices to stimulate buyers. This is a good example of a situation where supply is above demand.
On the other hand, imagine that it was a bad year for apple farmers and that there is a deficit of this fruit on the market. To fulfill their needs, buyers will quickly empty warehouses if the price remains at the same level. When retailers see the growing demand that goes along with the limited supply, they will definitely raise prices.
When it comes to Forex and other financial markets, it works pretty much the same. If demand for a particular currency is rising and the supply remains the same or is cut, the price of this currency is likely to grow. When supply is growing (after a central bank’s decision to cut rates or launch a QE round) and it overlaps demand, the currency price goes down.
By understanding the basics of this supply and demand concept, it will be easier for you to learn more about how traders use it in their activities. Your main goal in trading is to understand whether demand is going to prevail or, on the contrary, whether supply will weigh over demand. Fundamental analysis offers a lot of tools that you can use to see those tendencies and predict price fluctuations in the long term.
Fundamental Analysis indicators

If you read about technical analysis you know that there are so-called indicators there that help traders follow trends and even predict their reversals. When it comes to fundamental analysis, you can also rely on some indicators that will allow you to put things into perspective and understand where the balance between supply and demand may shift.
Find the key indicators below:
- Central Banks Decisions. This is the most important indicator that you should follow, as central banks are responsible for monetary policy and, thus, they can increase or decrease liquidity in the markets. When they decide to hike rates, this means that they want to decrease liquidity, which, in turn, will lead to a situation where demand is likely to be higher than supply. Once a central bank cuts rates, on the other hand, this adds liquidity to the markets and, therefore, the currency is likely to drop in price.
- Gross Domestic Product or GDP. This is another key indicator that influences currencies the most. It shows how a particular economy performed over a certain period. However, GDP data is a lagging indicator, which means that market participants are already aware of the current GDP growth perspective.
- Consumer Price Index or CPI. This indicator is calculated by averaging price changes over time in a basket of consumer goods. The CPI shows consumer inflation, which is important as central banks set their inflation targets and adjust monetary policy according to them. If inflation is above the target, central bankers can hike rates to curb it, and vice versa, if it is below the target level, they may cut rates to stimulate consumption.
- Producer Price Index or PPI. Another side of inflation is the producer price index. It can be used by economists and traders to forecast consumer inflation. If the PPI growth speeds up, you can expect the same for the CPI in the future. On the other hand, in times when PPI slows down, you can expect CPI to slow down as well.
- Institute of Supply Management Purchasing Manager Index (PMI and ISM). This index comprises surveys of 400 manufacturing purchasing managers that cover the most important fields, including inventories, employment, speed of deliveries, production level, and new orders from customers. This is a very important index that reflects the current state of the economy and is released in advance.
- Labor Market Data. The unemployment rate and non-farm payrolls reflect the situation in the labor market. Those are indicators that illustrate how healthy the economy is. They are very important and can trigger huge market fluctuations, especially if their final results differ from forecasts. Non-Farm Payrolls are the key indicator for the US labor market, which represents the number of jobs added, excluding farm and government workers.
Fundamental Analysis vs. News Trading: What is the Difference Between Them?
Fundamental analysis and news trading are totally different concepts. While news is an integral part of fundamental analysis, you need much more than simply guessing whether the final reading of a particular macroeconomic indicator is above or below the forecasts.
Fundamental analysis is, first of all, about analysis. The key idea is to predict the behavior of market participants by using macroeconomic indicators as tools. And the most important thing about fundamental analysis in Forex is to predict how central bankers will react to a set of the most important data. Here is the key to success.
Fundamental analysis differs from news trading in its basic concepts and time intervals. While news trading is limited to a couple of hours, fundamental analysis allows you to find mid and long-term trends that can develop for months and even years. Therefore, this type of market prediction is relevant only to Forex traders.
When it comes to news trading, you do not need all those long-term tendencies to analyze. The only thing that matters for you in this case is the divergence between the previous, forecasted, and current readings of a particular indicator.
The basic news strategy is to buy digital contracts or buy/sell a forex currency pair depending on the results of the particular data release. If you see that it is better than forecasted, the currency is likely to grow, while, on the other hand, if it is worse than forecasted, the currency is likely to plunge.
Central Banks Decisions: How They Affect Forex Currencies
First of all, you should know that there are two main types of monetary policy. Expansionary policy occurs when monetary authorities decide to stimulate the economy. During periods of expansionary policy, central banks maintain lower interest rates and sometimes launch so-called quantitative easing, which increases the money supply in the economy.
As you can guess, when the money supply increases, it overlaps with the demand in most cases and pushes the currency price lower. A good example of expansionary monetary policy was during the anti-COVID measures that were taken in the USA, Europe, Australia, and other countries and regions. The rates were close to zero or even negative, which stimulated demand for goods and services even during the COVID period.
Nowadays, most economies that use this expansionary zero-rate “dovish” approach suffer from excessive inflation. On the other hand, most economies struggle with recessions, which do not allow them to significantly hike rates. This dilemma brings uncertainty to the monetary policies of most countries.
When it comes to the stock market, expansionary policy creates additional supply for various equities. This is due to the fact that loans become cheaper, and commercial banks as well as investment funds have more cash on hand to spend on stocks.
Contractionary “hawkish” policy, in turn, maintains greater interest rates, which cuts the money supply. It is used by central banks to slow down inflation and may provoke recession as one of the collateral consequences.
Fundamental Analysis: How It Works
Now it is time to see how fundamental analysis works. As we have already mentioned, everything revolves around the central bank’s decisions about monetary policy. Therefore, the main goal of a trader when they conduct fundamental analysis is to predict how a particular event can impact a central banker’s opinion about future monetary policy changes.
First, you should look at current rates and monetary policy. If the rates are low and there is a quantitative easing program, for instance, such a policy normally leads to the currency’s downtrend. In addition, you should learn what conditions have led central bankers to make those decisions. For instance, this may be inflation, which is below the targeted level, or a recession.
When you have done this primary analysis of the current situation, you can proceed with following news and revealing macroeconomic tendencies that will help you understand the possible future decisions of central banks and, therefore, price movements.
Once the situation begins to change for the better, the downtrend stops and reversal signals may appear on the charts. For instance, if inflation starts to grow and reaches the targeted level or even goes beyond it, you can expect the central bank to be more “hawkish” during the next meeting or even over a longer period.
In general, if you expect a central bank to be “hawkish”, this means that the currency is likely to grow over time in the mid and even long-term, and vice versa, if you think that central bankers are more “dovish”, you can expect the currency to go down over time.
Fundamental Analysis and Market Expectations
Price movements can be caused not only by pieces of data but also by expectations themselves. Traders and investors are buying or selling assets in advance before a key announcement or data release. As for events themselves, those can be central banks’ meetings, CPI data, labor market statistics, etc.
Price can make hundreds of pips on expectations before the event. The reason for this is that a lot of traders and investors are preparing themselves for key data releases or officials’ commentaries. If data figures meet expectations or officials’ comments go along with market hopes, then there may be no reaction during the data release itself.
However, if the final result fails to meet expectations, then another major price movement can occur. And this time, you will have another great opportunity to make money.
It should be mentioned that many huge market players do not wait for the data to be released to make their decisions. They tend to buy or sell assets beforehand. Their decisions are based on a so-called “consensus system,” which is a kind of forecast that is made before the main data release. For instance, you can find two figures in most macroeconomic calendars that demonstrate previous data readings and forecasts. A lot of market makers and heavy players tend to squeeze the maximum out of the market when they see this consensus prediction.
All the above is one of the reasons you should avoid news trading. Even if this strategy is popular among traders, it has a lot of drawbacks, and one of them is that expectations can create much more market buzz than the main data release. Therefore, you can place a trade on the eve of the data release and expect significant price movements, but once the data becomes public, nothing extraordinary may happen. This is due to the fact that a particular macroeconomic indicator or officials’ speeches were played by the market in advance.
What Should I Know to Use Fundamental Analysis
Unlike technical analysis, which is the fastest and easiest way for traders to jump-start trading, fundamental analysis requires a lot of knowledge. The basic textbook that you should read from cover to cover is Economics, which can be found in many variations nowadays. Along with this textbook, there are plenty of other books that are worth looking through.
The main thing that you should get from all those books is how economics works and how supply and demand impact price fluctuations.
Example of Using Fundamental Analysis
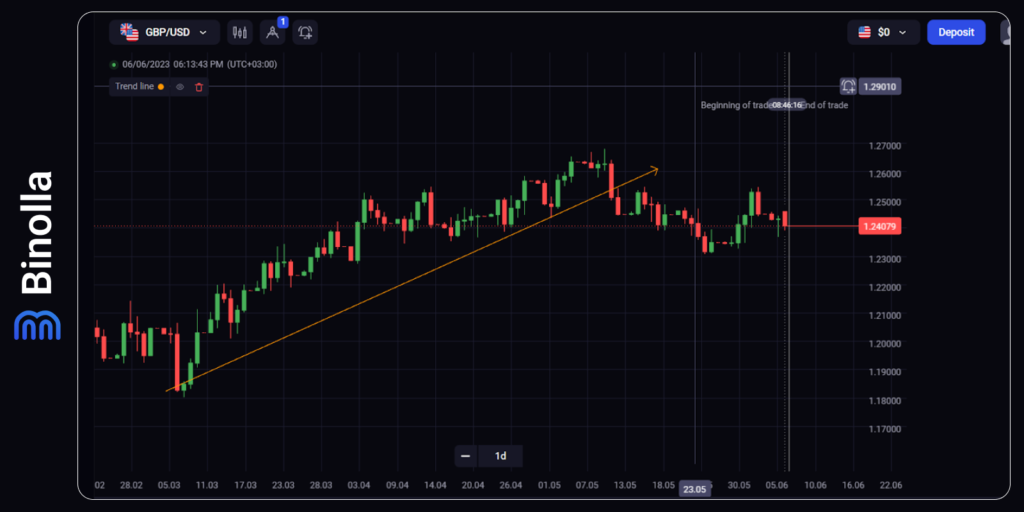
The chart above demonstrates an uptrend in GBP/USD that started in March 2023. The uptrend was provoked by several factors, such as the bankruptcy of some US banks as well as the slowing down of US economic growth.
Investors and traders considered the possibility that the FOMC is likely to stop hiking rates and even cut them in the near future. Therefore, the US dollar was under pressure while GBP gained some support. Moreover, the Bank of England had a tightening strategy, which affected the currency pair as well.
Key Differences Between Fundamental Analysis
There are two main types of analysis that you can use to predict price movement directions. Both fundamental and technical methods are very useful. Here is how they differ from each other:
- Fundamental analysis aims at finding global trends and long-term price fluctuations, while with technical analysis, you can predict even the shortest price movements. Fundamental analysis is useless for short-term traders, as you can’t even see those global price movement directions on smaller timeframes. Therefore, technical analysis can be used by all categories of traders (you can even apply this methodology for long-term trading), while fundamental analysis can be conducted to reveal mid-term and long-term trends only;
- Fundamental analysis considers macroeconomic events and financial trends to reveal major price movements, while technical analysis evaluates price movements via various tools that use calculations or can be drawn on charts. Therefore, technical analysis is more illustrative, as you can see the results of those calculations on the chart in the form of lines, curves, shapes, etc. Fundamental analysis is not illustrative at all;
- Fundamental analysis considers both past and present data of the stock, while technical analysis can only give you past data;
- Fundamental analysis can help understand whether a particular asset is overvalued or, on the contrary, undervalued by the markets. However, this doesn’t mean that you will have a clear signal when to buy or sell. Sometimes, traders using fundamental analysis need no entry points at all as they join a current price movement and wait for some fundamentals to hint at a reversal. When it comes to technical analysis, you will have clear entry points that will tell you when to buy or sell a particular asset.
Fundamental Analysis Pros and Cons
Here are some key advantages of using fundamental analysis:
- This methodology is based on market data and commentaries of officials, which makes it a very valuable tool. By using fundamental analysis, you can understand the reasons for the price to choose a particular direction. Therefore, you can gain insight into the very heart of the market;
- Fundamental analysis allows you to reveal long-term price trends, which, in turn, gives you the full picture of what is going on in the markets;
- When using fundamental analysis, you can rely on huge arrays of data that allow you to confirm your assumptions about a particular asset and its price forecasts.
Even with such strong advantages, fundamental analysis comes with some serious disadvantages:
- The first and main weak point of this analysis method is that it requires a lot of knowledge. You can’t simply look through data and make your assumptions. You need to understand how a particular data release may affect the asset. Without this clear picture of all the connections between various macroeconomic indicators or central banks’ solutions, you can’t go any further with fundamental analysis;
- This method is very time-consuming. You will spend hours and days looking through all the available data to reveal where it can lead the price in the future;
- Fundamental analysis is not illustrative, which makes it harder for traders to reveal major trends and make assumptions.
Fundamental or Technical Analysis: What Is Better?

Both fundamental and technical analysis types are very useful in trading. Therefore, instead of thinking about which one is better, traders can combine them in different ways:
- Fundamental and technical analysis can be used together to forecast major trends. After analyzing macroeconomic data, you can take a look at charts to find technical analysis signals. If both go in confluence, then you can be more sure about your future decisions;
- Traders can create a list of assets that they are going to trade using fundamental analysis. For instance, you can pick those assets that will be affected by the upcoming market data releases. Then you can switch to charts and use technical analysis for further research;
- A combination of fundamental and technical analysis can be useful in finding exit points as well. If fundamentals are positive for a particular currency, but technical indicators or other systems show reversal signals, then you can hold your current position as a technical correction if possible instead of a full-fledged reversal;
- Using fundamental analysis may be helpful for traders who want to buy or sell on breakouts and catch major mid-term trends.
Conclusion
Fundamental analysis is widely used by traders and investors to predict major trends in stocks, currencies, commodities, indices, and even cryptocurrencies. When applying this method, you are trying to understand whether current fundamentals go in line with the major price movement direction.
When conducting fundamental analysis, traders use various sets of data that allow them to make assumptions on the future interest rate or evaluate the intrinsic value of stocks when it comes to investing.
Before starting to use fundamental analysis in your trading routine, you should learn a lot about the interconnection between various pieces of data and central banks’ decisions.
FAQ

What is the Main Indicator in Fundamental Analysis?
The main indicator in fundamental analysis is the interest rate. This rate defines how cheap or expensive credits are. If the interest rate goes up, the currency becomes more expensive, while during periods of low interest rates, the currency price plunges. When it comes to stocks, apart from general macroeconomic analysis, you should go deeper and make some calculations to reveal the intrinsic value of a particular stock.
How to Master Fundamental Analysis?
To be able to apply fundamental analysis to trading, you should understand how economic, financial, and political events will impact a particular asset. Therefore, you should be good at macroeconomics and politics in order to make predictions. Moreover, you should also study the interconnection between various sets of macroeconomic data and possible central banks’ decisions.
Is Fundamental Analysis Useful for FX Traders?
Yes, it is. This type of market analysis allows traders to reveal major fundamental trends by analyzing the coming macroeconomic data. While it is not necessary to use fundamentals in your trading routine, those traders who combine both technical and fundamental analysis are considered more successful.
What is the Key Difference Between Fundamental and Technica Analysis?
Fundamental analysis studies the influence of macroeconomic data and politics on asset prices, while technical analysis helps reveal tendencies by using calculations and drawings that are applied to charts.







