Gaps in Trading: How Traders Can Benefit From Gaps in Their Daily Routine

Gaps are the distance between the closing price of the previous candlestick and the opening price of the next one. Normally, they appear between sessions, but in some cases, when key fundamentals are released, gaps may occur in the middle of the trading day. While they are rare guests on the currency charts, they can be frequently found in stocks, which is mostly due to the fact that shares’ trading sessions are brief. By reading this article, you will discover more about price gaps, their types, their nature, and how to use them in digital options, Forex, or stock trading. If you are ready to start trading, create an account at Binolla now!
Contents
Price Gaps Basics
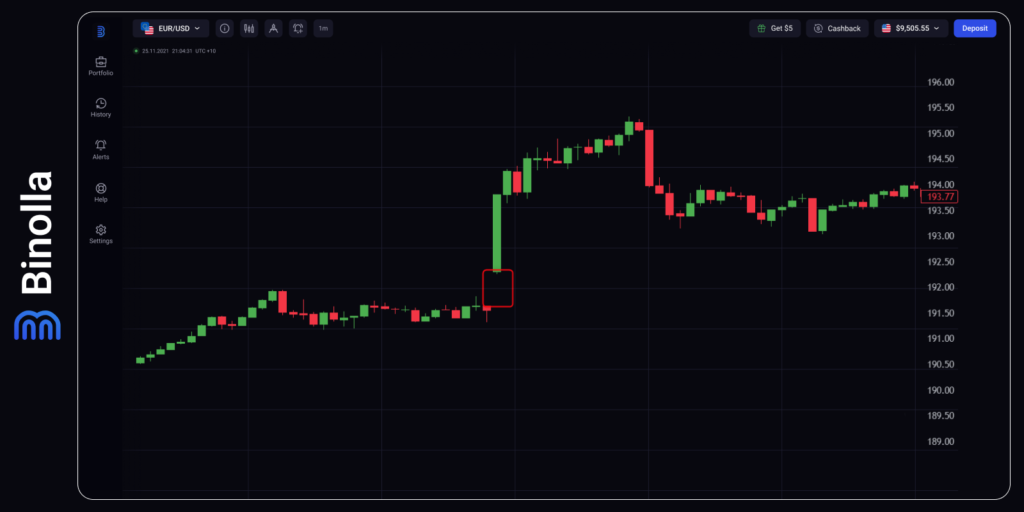
Price gaps refer to situations on charts where the closing price of the previous candlestick is higher or lower than the opening price of the following one. Gaps may appear on charts due to various reasons, including technical, fundamental, market sentiment, etc. If an unexpected event, such as a change in interest rates or significantly better/worse results of data release, a gap may take place. Gaps may also occur due to technical reasons when the price hits an area where lots of stop losses were placed.
Importance of Gaps in Trading
By using gaps, traders can find the idea about the price movement. You can use gaps along with other technical and fundamental analysis tools to predict price fluctuations. While in most cases, gaps are not signals themselves, they will provide you with some clues that you can use in your strategy to improve your trading results.
Whether you are trading digital options, Forex, or stocks, finding a price gap can be a big luck as it will help you predict further price fluctuations.
Types of Gaps in Trading
The are four key types of gaps that you will find on charts during your trading career. Some of them are more frequent, while others may be rare guests. Anyway, knowing what exact gap you have in front of your eyes may be very helpful.
Common Gaps
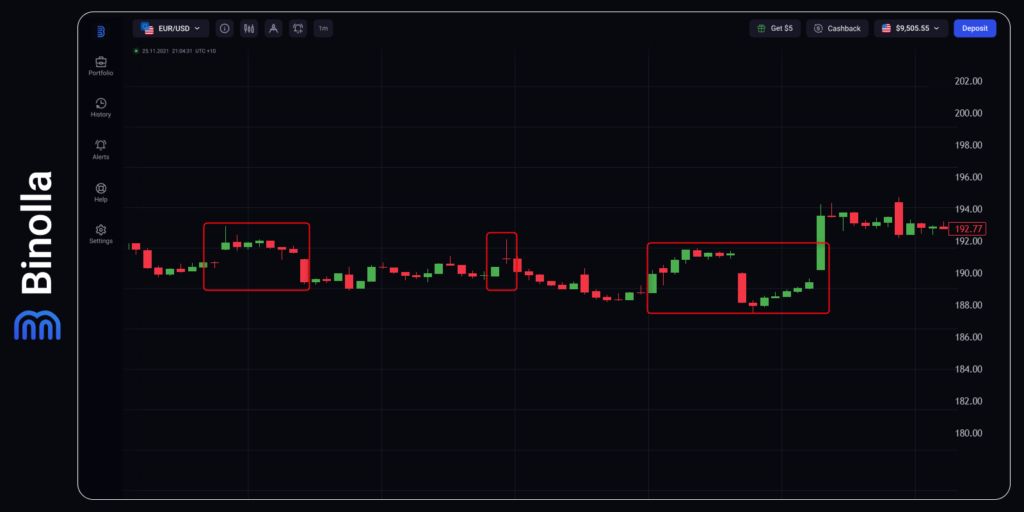
These gaps can be found frequently and they are very small in most cases. They can mostly be found in relatively tight ranges and are accompanied by low trading volumes. These gaps are more likely to be filled than most others as they are caused by normal price fluctuations.
Breakaway Gaps
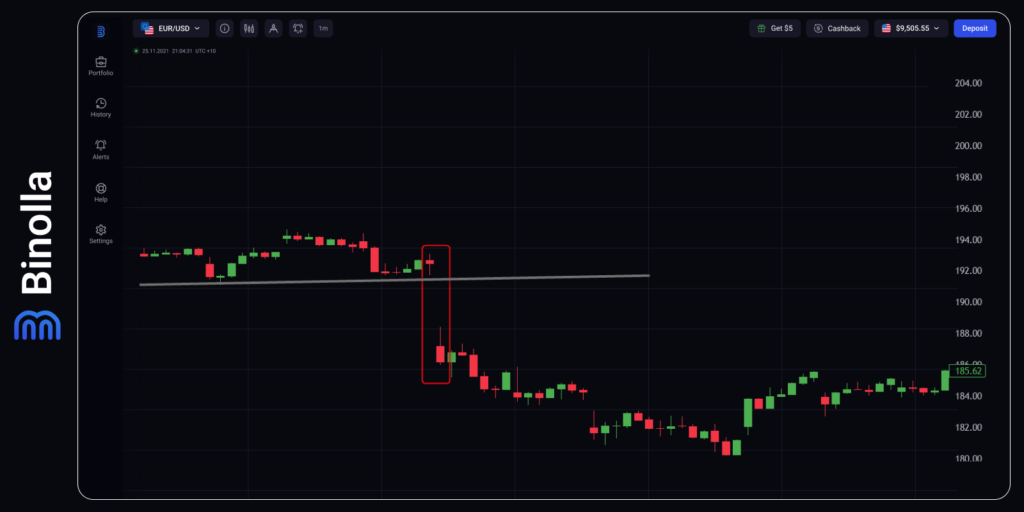
This type of gap occurs when a price breaks a certain level. It may indicate a significant change in market moods and even be a signal of a new trend to start. Normally, breakaway gaps are wider than common ones and they are accompanied by higher trading volumes.
Runaway Gaps
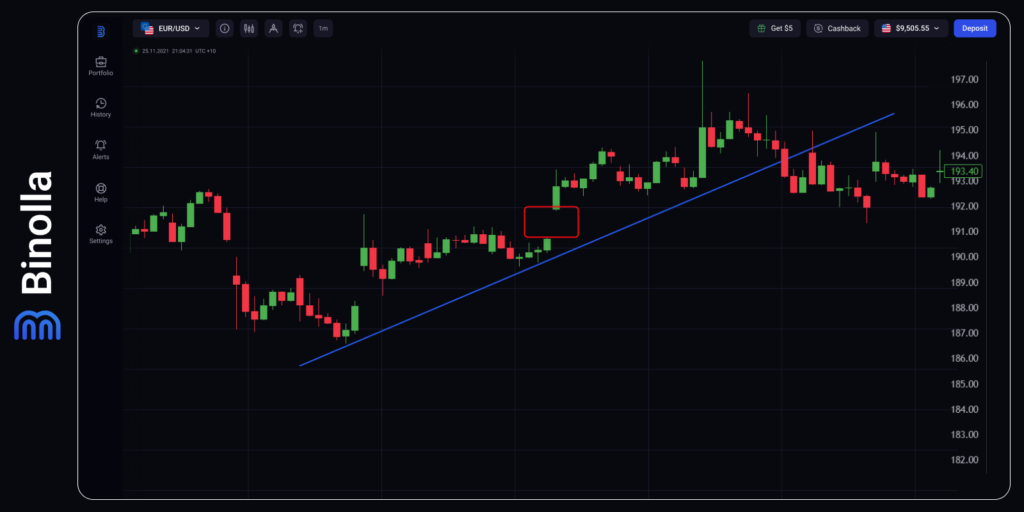
Such gaps can be found in the middle of the trend and they always indicate a continuation of the price movement direction. Similar to the previous type, such gaps are associated with higher trading volumes and significant price movements.
Exhaustion Gaps
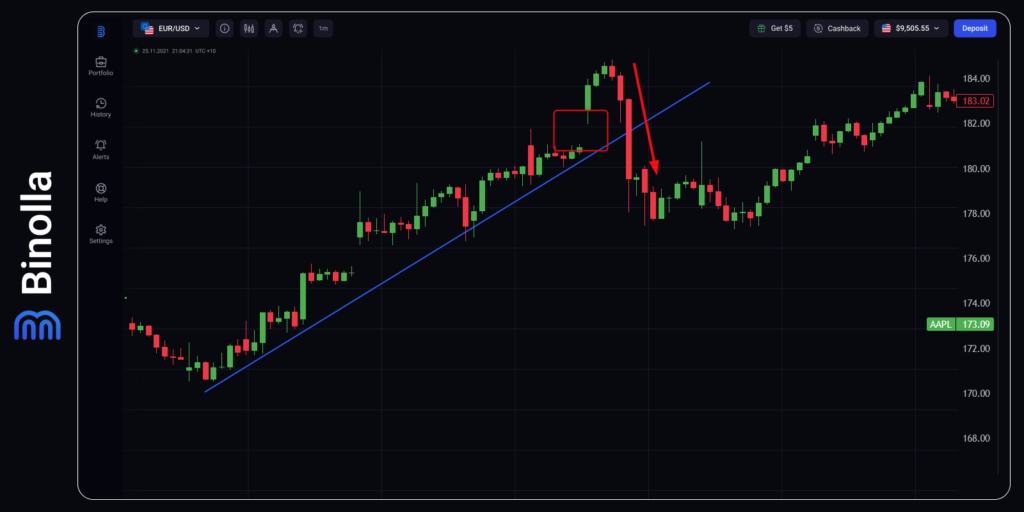
Unlike the previous one, this type of gap appears at the end of the trend. Trading volumes are normally high, however, market moods are already changing. This type of gap is likely to be filled as can be seen in the example above.
Factors to consider with trading with Gaps
In addition to classifying gap types, traders should factor in several considerations when crafting a gap trading strategy. Here are some crucial points to ponder:
- Volume and Liquidity. Assess the volume and liquidity of the security being traded. Higher volume and liquidity imply a smoother gap, given the increased participation in trading;
- Market Trend. Take into account the prevailing market trend. In a strong trend, gap fills may be delayed or might not occur at all. Conversely, in sideways or ranging markets, gap fills are more probable;
- Time Frame. Consider the time frame of the gap. A gap on a daily chart may require more time to fill compared to one on an hourly chart. Align your strategy with the chosen time frame accordingly;
- Technical Analysis. Utilize technical analysis to pinpoint crucial support and resistance levels that could influence price action during a gap fill. These levels serve as guideposts for trade entry and exit decisions;
- Fundamental Analysis. Incorporate fundamental analysis to enrich your gap trading methods. Evaluate earnings reports, economic indicators, and other news events that could impact the market, aiding in identifying potential gaps;
- Risk Management. Prioritize risk management. Gap trading entails inherent risks, necessitating a robust risk management plan. Implement measures such as setting stop-loss orders, employing position sizing techniques, and adhering strictly to your trading plan.
By integrating these factors into your gap trading strategy, you can enhance your decision-making process and improve the effectiveness of your trades.
Gap Trading Strategies
In general, there are two types of strategies that traders can use when it comes to gaps. The first one is when a trader buys or sells digital options, Forex currencies, or stocks in the direction of the gap. The second strategy, in turn, allows traders to find entry points in the opposite direction when a gap is filled. Unlike the first strategy, the second one can be applied by FX and stock traders only.
Trading in the Direction of the Gap
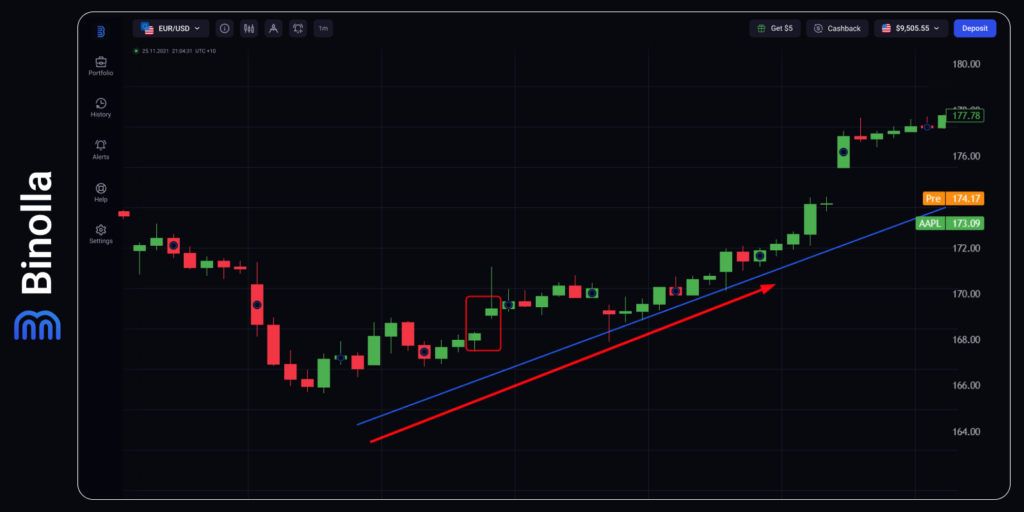
The first strategy is when a trader buys a Higher contract or purchases a currency pair/stock when an upside gap appears. The strategy is pretty much simple as you don’t need any other tools to apply except a trendline. Once you see a gap, you can enter the trade right away. The only condition is that the gap should be in the direction of the main price movement. In this particular case, we have an uptrend, which means that the best solution is to buy a Higher contract or to open long positions.
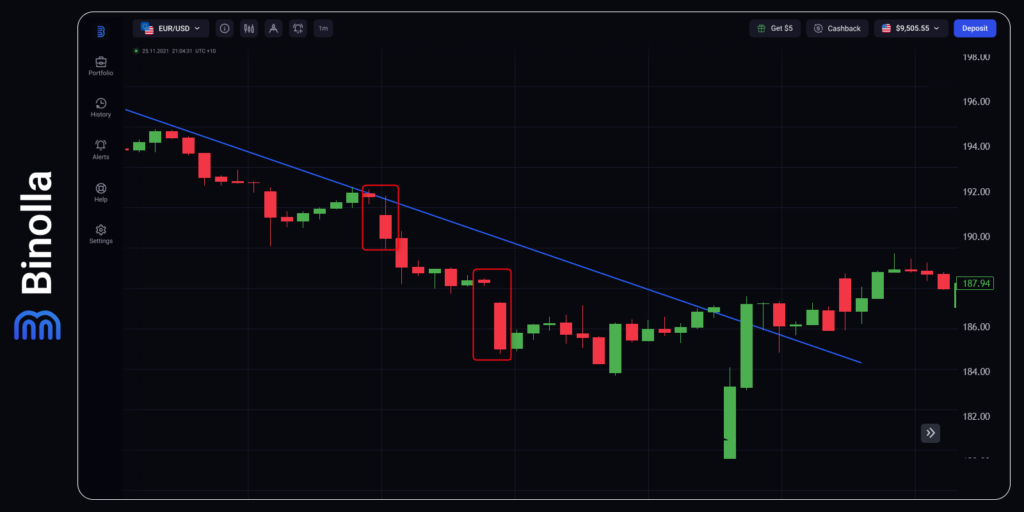
Another example is when the price goes along the downtrend. We have outlined two gaps where traders can buy Lower contracts or sell a currency pair/stock. The signal is the same, traders should enter the market once a gap appears.
Trading with the Gap-Filling Strategy
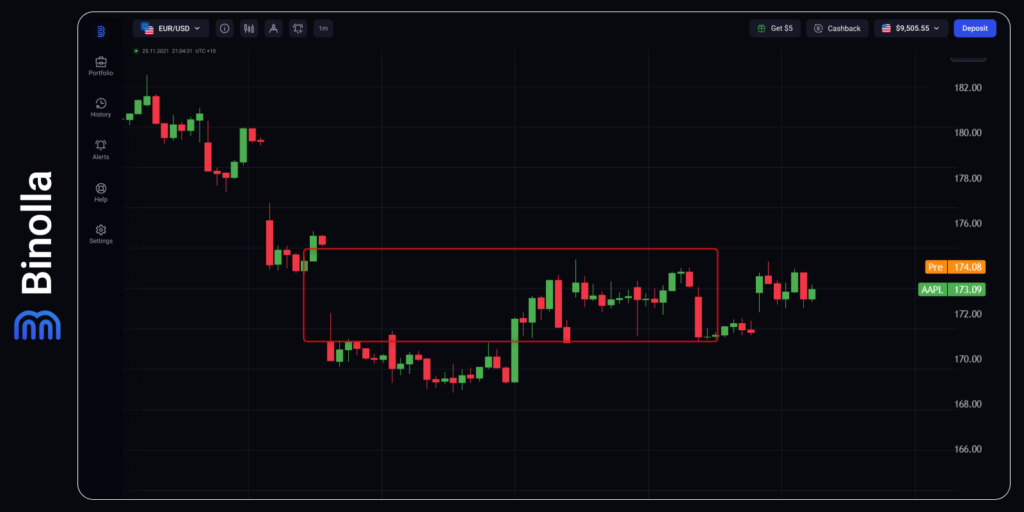
This strategy can be used by FX and stock traders only as it requires waiting until the gap is filled. Once a gap appears, traders should buy a currency pair or a stock and wait for the price to cover the distance. As you can see in this example, the price makes an attempt to go lower, but later it goes in the direction of the previous gap and fills it.
Recommendations
Trading with gaps can be a profitable strategy, but it requires careful consideration and risk management. Here are ten recommendations for trading with gaps:
- Understand gap types. There are three main types of gaps – common gaps, breakaway gaps, and runaway (continuation) gaps. Each type has different implications for price action, so understanding them is crucial;
- Identify significant gaps. Focus on identifying gaps that occur after important news events, earnings releases, or significant market developments. These gaps tend to have more trading opportunities and higher volatility;
- Confirm with volume. Always look for confirmation of the gap with high trading volume. High volume during a gap indicates strong market participation and increases the reliability of the gap signal;
- Wait for the gap to fill. In many cases, price tends to fill the gap, meaning it returns to the level where the gap originated. Consider waiting for the gap to be filled before entering a trade to increase the probability of success;
- Use technical indicators. Combine gap analysis with other technical indicators such as moving averages, trendlines, or oscillators to confirm trading signals and filter out false signals;
- Consider market context. Analyze the broader market context before trading with gaps. A gap in the direction of the prevailing trend is more likely to continue, while a gap against the trend may signal a potential reversal;
- Manage risk. Implement proper risk management techniques such as setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Gaps can be volatile, so it’s essential to protect your capital;
- Monitor news and events. Stay informed about upcoming news events and economic releases that could potentially cause market gaps. Being aware of these events can help you anticipate and capitalize on gap trading opportunities;
- Practice patience. Avoid chasing gaps or entering trades impulsively. Wait for a clear setup and confirmation before entering a trade, even if it means missing out on some opportunities;
- Review and learn. Keep a trading journal to record your gap trading experiences, including successful and unsuccessful trades. Review your trades regularly to identify patterns and improve your gap trading strategy over time.
Remember that trading with gaps carries inherent risks, and not all gaps will result in profitable trades. It’s essential to remain disciplined, and patient, and continuously learn and adapt your approach based on market conditions.
FAQ

What is a trading gap?
A trading gap occurs when there is a noticeable difference between the closing price of a security and the opening price of the next trading session. This creates a gap or “jump” in the price chart.
What causes trading gaps?
Trading gaps can be caused by various factors, including significant news events, earnings announcements, sudden shifts in market sentiment, or overnight trading activity in other time zones.
What are the different types of trading gaps?
There are three main types of trading gaps: common gaps, breakaway gaps, and runaway (continuation) gaps. Common gaps occur within the trading range and are often filled quickly. Breakaway gaps signify the beginning of a new trend, while runaway gaps occur in the middle of a trend, indicating its continuation.
How do traders typically approach trading with gaps?
Traders often employ gap trading strategies to capitalize on the price movement resulting from the gap. This may involve trading with the direction of the gap, waiting for a gap to fill, or using other technical or fundamental analysis techniques to determine entry and exit points.
What role does volume play in trading gaps?
Volume is an essential factor in gap trading. High volume accompanying a gap signifies strong market participation and increases the reliability of the gap signal. Traders often look for confirmation of the gap with high trading volume to validate their trading decisions.
What risk management strategies should traders consider when trading gaps?
When trading gaps, it’s crucial to implement effective risk management strategies to mitigate potential losses. This may include setting stop-loss orders, sizing positions appropriately, and adhering to a disciplined trading plan. Additionally, traders should be mindful of the inherent volatility associated with gap trading and adjust their risk accordingly.