Impact of Inflation on Digital Options Trading: Strategies for Hedging

Inflation is an important economic indicator showing a general increase in prices of goods and services. Forex and digital options traders focus on inflation as it has a direct impact on the central bank decisions. Therefore, this indicator has a direct impact on currencies, and, in turn, digital options and Forex trading results
By reading this articles, you will learn more about the mechanisms eroding purchasing power. You will also have an insight on how central banks react on higher and lower inflation. If you are ready to start trading, open an account at Binolla.
Contents
- 1 Inflation Basics
- 2 Inflation and Interest Rates: How They Are Interconnected
- 3 Key Inflation Fundamentals
- 4 Benefit from the inflation data now!
- 5 Key CPI Reports Around the World
- 6 Inflation and Digital Options Trading
- 7 Inflation and Forex Trading
- 8 Inflation and Stock Trading
- 9 An Example of How Inflation Data Release May Influence Currencies
- 10 FAQ
Inflation Basics
The rate at which the prices of goods and services rise in known as inflation. When inflation speeds up, one can buy fewer goods and services with one unit of currency, which decreases the purchasing power and the value of money. Traders can find inflation data in macroeconomic calendars. Normally, it is measured as CPI (consumer price index) and PPI (producer price index). Both track changes in prices for goods and services over time.
A lot of factors may influence inflation. They may include increased demand for goods and services, lower supply, higher producer prices, lower rates, etc. In simple words, if a customer has more funds at their disposal, they can spend more on goods and services, which, in turn, increases inflation.
Prices may also rise when the cost of labor, energy or raw materials becomes higher. Central banks monitor inflation and may adjust their monetary policy accordingly. Central bankers may increase interest rates when the inflation is high as well as cut them when inflation is decreasing.
The impact of inflation on the economy is wide. When the rate of inflation is moderate, the economy is growing. However, excessive rate results in lower investment and general uncertainty. When it comes to deflation, it results in decreasing consumer spending, which, in turn, leads to stagnation. Central banks balance between high inflation and deflation to maintain steady growth.
Inflation and Interest Rates: How They Are Interconnected
To cool down inflation or fight deflation, central banks adjust interest rates. When inflation is higher than expected by central bankers, they increase rates to reduce the circulating money. Higher interest rates curb inflation by discouraging individuals and companies from taking loans. In this situation spending and investment is cut. On the other hand, by cutting rates, central bankers unleash more liquidity by decreasing loans interests.
The main idea of adjusting interest rates is to manage prices. The decrease in costs of goods and services push inflation down until it reaches the central bank goals. The target set by central banks is the level which allows economy to grow along with price stability.
Curbing inflation of stimulating price growth in times of deflation is a very delicate process. Before achieving the goal, central bankers may be obliged to change interest rates several times. Raised too high, rates may lead to economic stagnation. Businesses may struggle with higher borrowing costs, which in turn, leads to reduced investment. Stagnation, in turn, may lead to higher unemployment rate and recession.
However, in case if a central bank raises rates insufficiently or they are lower, the inflation may increase and even lead to hyperinflation. Prices may increase significantly and erode purchasing power. This, in turn, results in devaluation of the currency. The inflation in Turkey was too high, which led to lira devaluation, which, in turn, resulted in significant economic problems for locals.
Therefore, central banks need to find balance between higher inflation rates and deflation in order to avoid economic turbulence. Officials constantly monitor the situation with prices and make careful decisions to ensure the interest rates contribute to stability and sustainable economic growth. Inflation and interest rates are interconnected and they play an important role for economic stability.
Key Inflation Fundamentals

Inflation is one of the key economic metrics that affects financial markets being an important indicator. The two main data releases that reflect inflation are CPI and PPI. By checking these indicators traders and investors can have an insight into price changes and make informative decisions about buying or selling a particular asset.
CPI is one of the most widely known indicators demonstrating inflation rate. The Consumer Price Index measures costs of goods and services in a fixed basket. It includes various foods and beverages, as well as other goods and services. In general, CPI reflects the living costs for households. When the indicator rises, the costs are higher, which means that the purchasing power is lower. Converserly, decreasing CPI reflects lower prices, which increases purchasing power.
When it comes to PPI, this indicator reflects the prices at which producers sell their goods. Unlike CPI, the Producer Price Index is based on the price changes at various stages of production, including the price of raw materials, labor, intermediate goods, etc.
The index is divided into three sectors, which include industry, commodity and stage of processing. The indicator provides economists, traders and investors with a broad range of data and a view of inflationary pressure on the economy. When the PPI indicator increases, the inflation is accelerating, which results in higher prices for goods, while the decreasing PPI slows down inflation and increases purchasing power.
Both indicators are released monthly by the Bureau of Labor Statistics of the US. Economists and investors wait for this release as they will have a view of the current situation in the US economy and will be able to make reasonable decisions.
The release of both indicators may trigger higher volatility in the financial markets. Traders and investors often use these reports to make trading decisions. If CPI slows down sharply, then a trader may expect the Fed to cut rates in order to stimulate price growth and consumer spending. On the other hand, when inflation grows sharply, this may lead to higher interest rates by the Fed as they are likely to try to curb prices of goods and services.
Understanding all the basics of both indicators will allow traders to make their own forecasts about the prices of various classes of assets. By checking the numbers, market participants can better navigate price fluctuations and make their own forecasts based on interest rates anticipations.
Key CPI Reports Around the World
CPI reports may differ depending on a particular region. They may have their own features. However, all inflation data releases have a serious impact on financial markets. One should know that the Consumer Price Index can be calculated on different formulas, which influences the final figures. Some of the key CPI reports are described in the following lines.
United States
The US inflation is calculated on urban areas. While CPI is important, the Fed mostly prefers the PCE (Personal Consumption Expenditures) Index over traditional CPI, which offers a more comprehensive measure of spending. With the PCE index, traders and investors can check a wider range of expenses and reflects accurate economic data.
- Region: North America
- Release Schedule: Monthly and yearly
- Issuing Agency: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
- Impacted Assets: USD, U.S. stocks, U.S. government bonds, and indices like US_Tech100
European Union
When it comes to ECB, the central bank looks at CPI data provided by all the states of the monetary union. This harmonized data uses averaged approach to reflect the consumer prices changes and economic size across the whole region.
- Region: Europe
- Release Schedule: Monthly and yearly
- Issuing Agency: Eurostat
- Impacted Assets: EUR, European stocks, government bonds of EU member states
United Kingdom
Inflation reports in the United Kingdom are managed by the Office of National Statistics. They provide economists and investors with the information on how consumer prices affect the UK economy.
- Region: Europe
- Release Schedule: Monthly and yearly
- Issuing Agency: Office for National Statistics
- Impacted Assets: GBP, EUR, British stocks, UK Gilts
Canada
Statistics Canada releases the Canadian CPI data monthly. It reflects inflation dymanics in Canada. The report affects a broad range of assets, including Looney and equities.
- Region: North America
- Release Schedule: Monthly and yearly
- Issuing Agency: Statistics Canada
- Impacted Assets: CAD, Canadian stocks, S&P/TSX, Canadian government bonds
Japan
The Consumer Price Index released by the Statistic Bbureau of Japan reflects economic health in one of the largest economies in the world. The data release affects various instruments, including the Japanese dollar, local stocks and government bonds.
- Region: Asia
- Release Schedule: Monthly and yearly
- Issuing Agency: The Statistics Bureau of Japan
- Impacted Assets: JPY, Japanese stocks, Nikkei 225, Japanese government bonds
China
The Consumer Price Index, released by the China’s government demonstrates the price dynamics and household spending. Apart from affecting the local currency, the CPI has an impact on stocks and bonds.
- Region: Asia
- Release Schedule: Monthly and yearly
- Issuing Agency: National Bureau of Statistics
- Impacted Assets: CNY, AUD, NZD, Chinese stocks, Shanghai SE Composite, Chinese government bonds
Australia
The inflation report in Australia is issued by the Australian Bureau of Statistics. It affects both AUD and financial instruments issued by local companies and government.
- Region: Oceania, Asia
- Release Schedule: Monthly and yearly
- Issuing Agency: Australian Bureau of Statistics
- Impacted Assets: AUD, NZD, Australian and New Zealand stocks and bonds
Inflation and Digital Options Trading

Digital options traders can use inflation data in their trading sessions. To capitalize on CPI or PPI data releases, you can simply watch the exact date and time of inflation data release and open a trade in one of the expected directions.
For instance, if you expect the US inflation rate to increase, then you can buy a Lower EUR/USD digital option as higher inflation in the United States will prevent the Fed from undertaking any easing steps or cutting rates. This will support the US dollar against other currencies, commodities and even cryptocurrencies.
On the other hand, when the US inflation data is lower, this is a signal for a digital options trader to buy a Higher EUR/USD contract as lower inflation rates mean higher probability that the Fed is going to cut rates, especially if inflation is below the target levels.
Inflation and Forex Trading
Forex traders have more options when it comes to inflation trading. They can both make simultaneous decisions and trade inflation as if they were using a news trading strategy or use this macroeconomic data to adjust their current long-term/mid-term positions and add new ones according to their long-term currency pair price expectations.
Forex traders normally buy a currency when inflation is rising as they expect the central bank to hold the rates or even hike them. On the other hand, when inflation decreases, especially below targeted markers, traders sell the currency.
When it comes to long-term predictions, they work the same way. If inflation’s trajectory is positive, one can buy the currency and hold the position for some time, especially if the positive inflation trend continues. However, if inflation decreases, a trader can sell the currency expecting the central bank to add liquidity during the upcoming meetings.
Inflation and Stock Trading
While the stock market is swayed by numerous factors, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) can play a crucial role in causing performance swings. For example, the Federal Reserve’s reactive measures to CPI data can have direct consequences on corporate profits and economic growth, leading to significant fluctuations in stock values.
When the Fed raises interest rates in response to higher CPI readings, the market often experiences dips or slows down as traders become more cautious and seek to hedge their positions. Should the central bank cut the rates reacting on lower inflation readings, the stock market considers this situation as a positive driver.
An Example of How Inflation Data Release May Influence Currencies
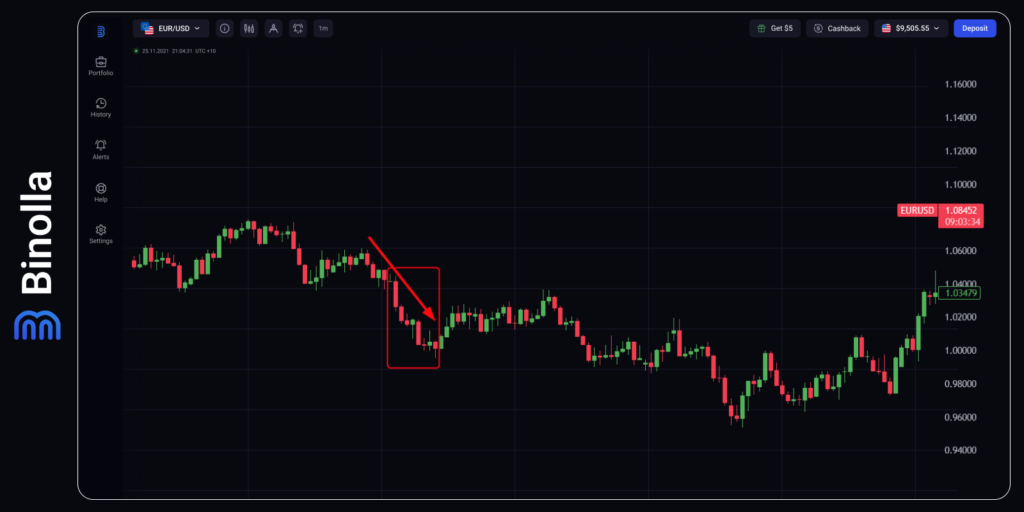
The annual inflation in the US has reached its local peaks in 2022 according to fundamentals. The data was published on July 13, 2022. Markets played it in advance with a series of bearish candlesticks in the EUR/USD currency pair.
Remember that there may be no instant reaction to the inflation data release. Moreover, as this example shows, the downtrend began in advance, before the US CPI y/y data was released and there was no significant movement at the exact moment of the data release.
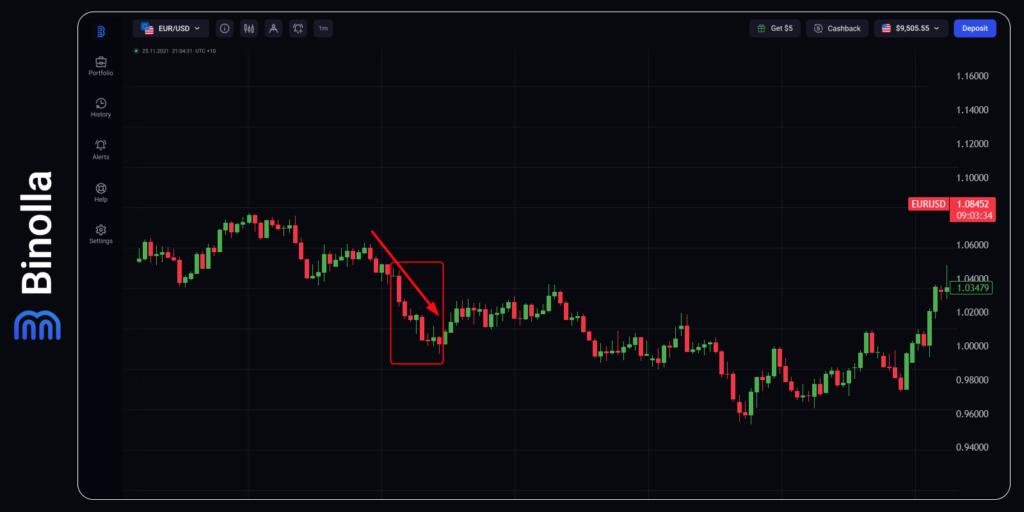
Another great example of how the market reacts to the inflation data illustrates the EUR/USD downside momentum after the release of the US CPI data on April 10, 2024. The inflation rate increased to 3.5% against 3.4% that was forecasted by economists. Moreover, it was 0.3 basis points higher as compared to the previous reading. Market participants reacted sharply to such difference between the current reading and the previous one. EUR/USD dropped significantly within a couple of hours. This was a great opportunity for both digital options and Forex traders to open short-term and mid-term short trades.
FAQ

Is Inflation Data Important for Trading?
Yes, it is. Inflation data reflects the economic health in a particular country. When inflation accelerates, central banks increase rates that supports local currency. In times of lower rates, the currency price drops.
How Central Banks React to Inflation?
Central banks hike rates when the inflation rate is higher. While inflation drops, central banks often cut rates to support economy.
How Do Traders Use CPI Data in Their Trading Sessions?
Traders follow the CPI reports in order to capitalize on them. For instance, when CPI is better than expected, market participants can buy a currency pair expecting the central bank to hike rates to curb inflation.
Is the PPI Data Important for Trading?
Yes, it is. The PPI data reflects the producer prices, which is one of the parameters of inflation. Higher producer prices will affect inflation.







