DXY Chart: The US Dollar Index Explained

The DXY dollar index is among the most popular and widely traded indices. It allows market participants to gain exposure to the global reserve currency directly without trading it against other currencies. Traders can use DXY directly by trading it with CFDs or digital options or understand the direction of the US dollar movement to use it in trading other assets. By choosing this type of asset, you will be able to capitalize on a variety of events that happen in the US economy, which is among the strongest in the world. In this article, we provide insight into the DXY index as well as give details on how to predict its fluctuations.
Looking for a reliable broker to trade? Join Binolla and enjoy all the features of the reliable platform right now!
Contents
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 What is DXY? The Basics of One of the Most Useful Indexes in the World of Financial Markets
- 3 The History of the Dollar Index
- 4 Start trading using this information now!
- 5 Key Factors that Affect the US Dollar Index
- 6 How to Predict the DXY Price Fluctuations: Technical Analysis
- 7 Conclusion
- 8 FAQ
Key Takeaways
- The US dollar index appeared right after the failure of the Bretton Woods system;
- Traders can buy and sell
- The index represents the value of the US dollar traded against the six major currencies;
- The DXY index price fluctuations are influenced by various macroeconomic and political events;
- Market participants can trade DXY via CFDs or digital options as well as use the chart to predict price fluctuations over a broad range of assets;
- Traders can use pure technical analysis to try to predict the USDX price fluctuations;
- The DXY index can be traded via futures and CFD contracts.
What is DXY? The Basics of One of the Most Useful Indexes in the World of Financial Markets
The dollar index is a special index that was created to measure the value of the US dollar against major currencies. The index was created right after the Bretton Woods agreement failure with the main purpose of tracking the dollar’s performance.
Once available as a future contract in the 1980s, it became widely popular among traders as the contract for difference.
The USDX is measured against the following currencies:
- Euro (57.6%);
- Japanese yen (13.6%);
- Pound Sterling (11.9%);
- Canadian Dollar (9.1%);
- Swedish Krona (4.2%);
- Swiss franc (3.6%).
In the pre-Euro era, the dollar index was calculated against the currencies that were listed above except the Euro, including the West German mark, French franc, Italian lira, Dutch guilder, and Belgian franc. The formula for calculating the DXY index is quite simple. To check the current index value, you need to multiply all currencies with their percentage weight.
USDX = Percentage * current currency price
Happily, you don’t need to conduct any calculations on your own, as the index is calculated automatically every 15 seconds based on the underlying assets.
The History of the Dollar Index
After the Second World War, the Bretton Woods agreement was signed. It required countries to guarantee the convertibility of their currencies to the US dollar to around 1% of fixed parity rates. The Bretton Woods system established a tight connection of the US dollar with gold. The American currency was convertible to gold at $35 per ounce. The United States had a responsibility to keep this convertibility, which means that every holder of the US dollar can exchange money for gold. The International Monetary Fund was created to monitor exchange rates and lend reserve currencies to countries with deficits.
This system was abolished in 1971 as American President Nixon ended convertibility. The US dollar wasn’t pegged to gold anymore. The index appeared in 1973 and was introduced to the Intercontinental Exchange, which was the forex predecessor.
The USDX price fluctuated freely according to the supply and demand of the currencies that are used in its formula. Here are some key milestones of the US dollar index.
Oil Сrisis of 1973
The first key milestone in the US dollar history was in 1973, following the creation of the index. The United States has supported Israel in the Yom Kippur war, which led to protests from OPEC. The organization decided to establish an embargo and stop supplying the US with petroleum. Moreover, OPEC has also conducted a series of production cuts to avoid overproduction.
The price of black gold has increased significantly from $2.90 before the embargo to $11.65 per barrel, which increased the price of gasoline in the United States.
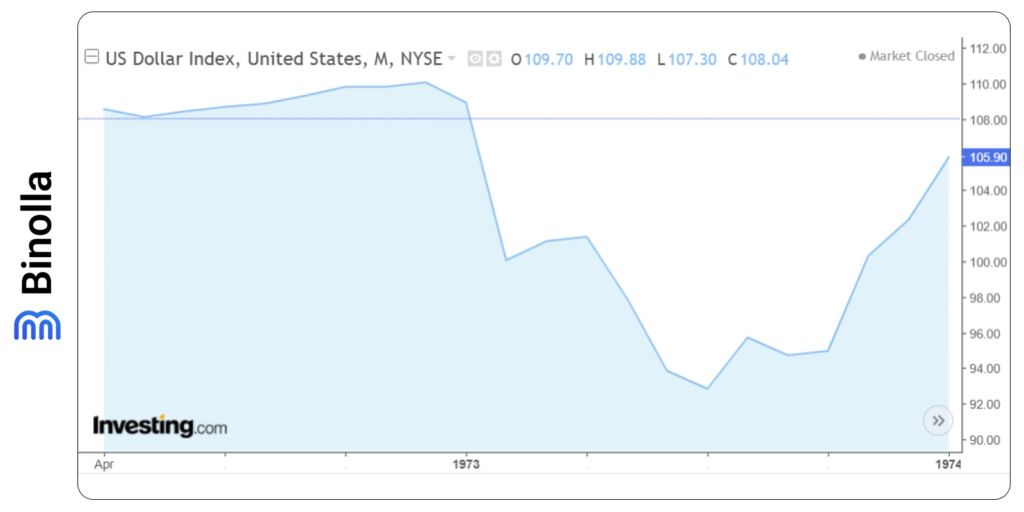
The oil crisis also led to a sharp US dollar decline from about 110, which was the peak at that moment, to less than 94. Commodity prices increased by 10%, which triggered inflation in the United States. The situation with the US dollar index stabilized a bit by the beginning of 1974 when the index rose to 105.
Plaza Accord of 1985
Another key milestone in the history of the US dollar index was in 1985. The Plaza Accord was signed in New York City and named after the hotel where the meeting took place. The idea was to push the US dollar down. The document was signed by the United States, Japan, and Germany. According to the accord, these countries implemented some measures to push the greenback down to stimulate the US economy.
The United States pledged to reduce its federal deficit, while Japan and Germany were to boost domestic demand by implementing tax cuts. All parties of the agreement agreed to intervene in currency markets to correct current account imbalances.
The reason for signing the agreement was the appreciation of the US dollar, which gained over 47% between 1980 and 1985. The strong dollar pressured US manufacturing as imported goods were way cheaper. The agreement was lobbied by major manufacturers such as Caterpillar and IBM.
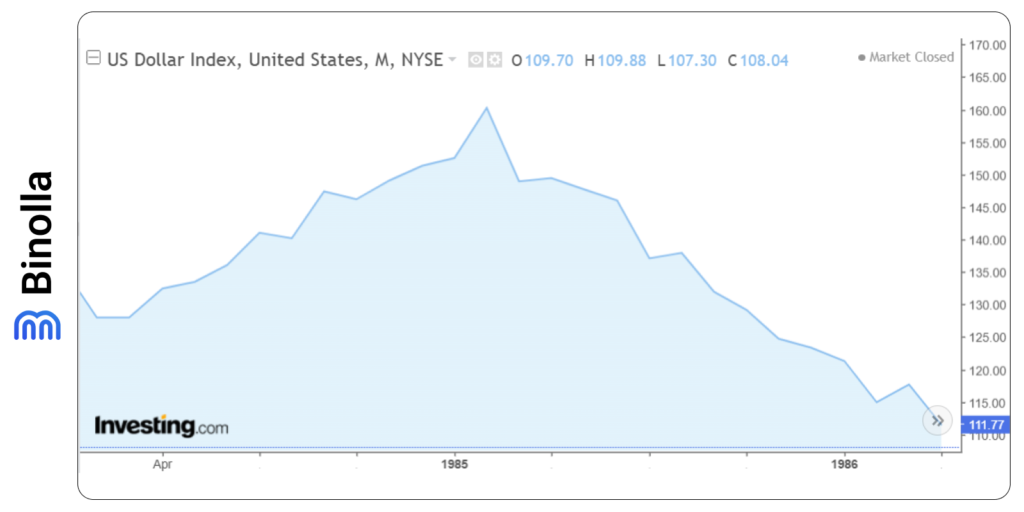
After the agreement was signed, the US dollar index moved down from over 160 to 110 by mid-1986 and even lower in the following years after breaking the 100 psychological level.
The Financial Crisis of 2008
Historically, low interest rates were among the main reasons for the financial crisis that took place in 2008. The ultrasoft monetary policy by the Fed led to the housing price bubble. However, everything began with good intentions. The Federal Reserve decided to cut rates following the dot-com crisis from 6.5% to 1% by June 2003.
The main goal was to stimulate businesses and customers. However, such a step resulted in inflation in the housing market as borrowers used low mortgages actively to buy homes. Moreover, banks were engaged in this game as well, and they provided loans to those, even when poor or no credit history at all, approaching the crisis.
The Fed began to raise rates in 2004, and by 2007, the rates reached 5.25%. Home prices began to fall by early 2006 in response to more expensive loans. This was a stressful situation for those who bought houses within the period of lower rates, which led to a lot of bankruptcies by 2007.
The crisis was already evident in 2007, and banks started to announce significant losses. It was time for the Federal Reserve and other central banks to step in and provide billions of dollars to help banks survive in this situation. Moreover, the Fed decided to cut rates by 75 basis points in January 2008. Later, in 2008, the Wall Street bank Lehman Brothers collapsed and marked the largest bankruptcy in US history.
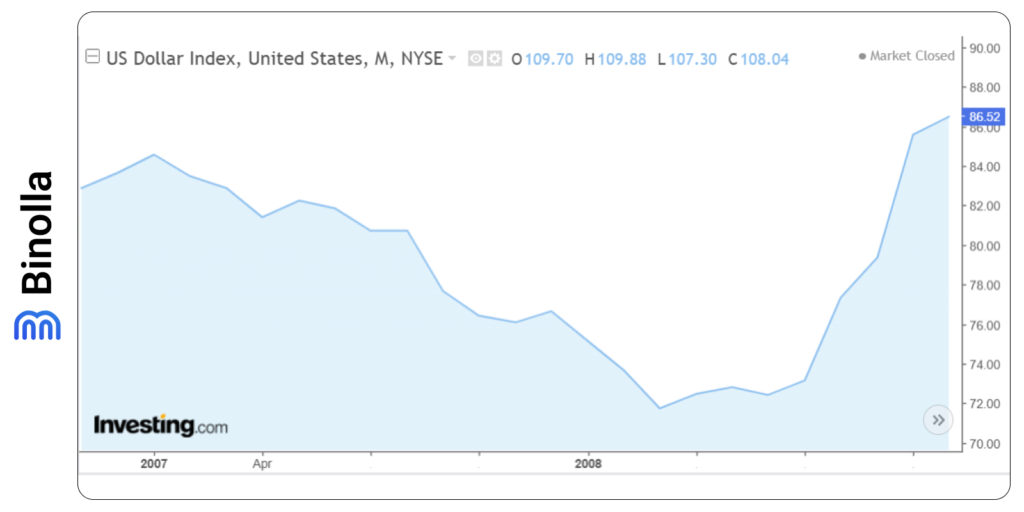
The steps that the Federal Reserve has taken led to a significant US dollar depreciation. The index fell from over 84 to below 72 within a year and then started to rise to over 86 in 2009.
The COVID-19 Pandemic
The next milestone occurred in 2020 during the active phase of the pandemic. The global shutdown, which was among the main measures in most countries, led to a global recession that, in turn, stimulated central banks to cut rates.
The US dollar initially rose in the early stages of the pandemic but moved lower once the rates were cut to almost 0%.
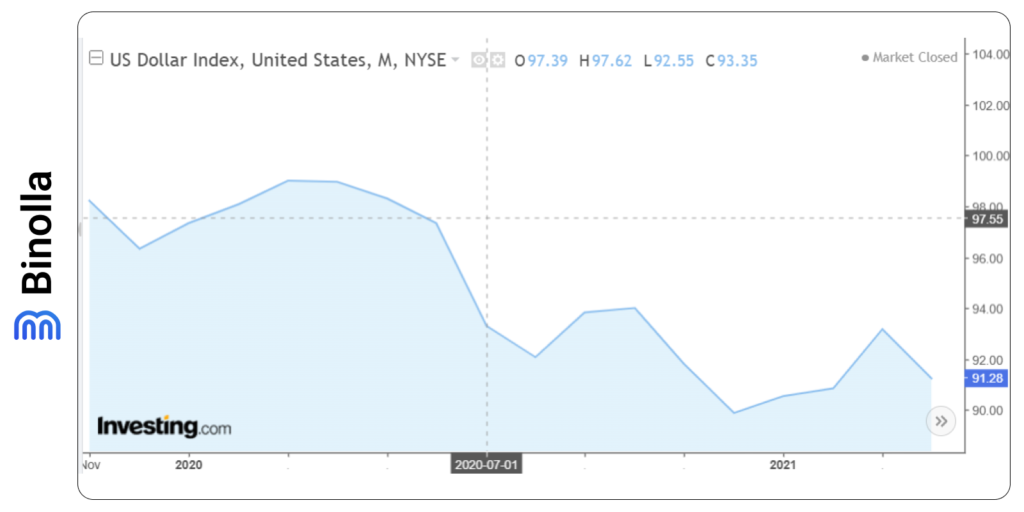
The US dollar index has almost reached 100 during the early stage of the pandemic, as the US dollar was used as a haven asset. However, after the Fed cut rates in early 2008, DXY moved down to below 90.
These were the key milestones in the history of the US dollar index. By further reading this article, you will know the main drivers that influence the USDX price fluctuations.
Key Factors that Affect the US Dollar Index
The US dollar quotes are affected by several factors that may trigger both uptrends and downtrends. Similar to other currencies, the dollar index reacts to central bank decisions, macroeconomics, and other factors that will be described below.
Federal Reserve Activities
The US dollar is issued by the Federal Reserve and is regulated by this central bank. Therefore, any steps from the Fed may trigger sharp price fluctuations. The Federal Reserve sets the target rate, which serves as the base interest rate for controlling the money supply in the United States.
When the rate is higher, loans become less attractive for customers, while bank deposits and savings in the US dollar increase. By increasing the federal funds rate, the Fed tends to control inflation and push it down at the cost of economic slowdown.
While the inflation rate is at target levels and the economic growth is slow, the Fed may cut rates to stimulate business activity. By doing this, the Federal Reserve decreases the cost of loans and makes saving in the US dollar less attractive. Customers spend more money, and the inflation rate becomes higher. In this situation, the US dollar depreciates.
Apart from the interest rate, the central bank has another option, allowing it to affect the economic growth and the US dollar quotes. By launching a so-called quantitive easing, the Fed adds liquidity to the financial markets and stimulates economic growth but risks seeing inflation rise.
Macroeconomic Factors
The key macroeconomic indicators that are released in the United States may also affect the US dollar index both positively or negatively. The rising GDP data, for instance, may attract USD buyers as there are fewer chances that the Fed is going to cut rates in this situation. A lower GDP growth rate or recession may lead to the US dollar depreciation as market participants will price in the future interest rate cuts. Some of the most important macroeconomic data releases include:
- Inflation. The rate at which the currency loses its purchasing power over time. The target inflation set by the Federal Reserve is 2-3%. If the inflation rate is above this level, the Fed is likely to hike rates to make inflation return to its target rates. Lower inflation or deflation may also be harmful as it shows that the business activity is low. To stimulate the inflation growth, the central bank may cut rates and launch a QE program;
- Employment. The unemployment rate is one of the key indicators demonstrating the economic health. The higher unemployment rate shows that there are some issues in the economic situation, and business activity is slower. Therefore, to stimulate employment and economic growth, the Fed may cut rates if inflation levels allow it to do it;
- Leading indicators. Manufacturing and services PMIs are very important for traders who want to analyze the DXY index as they show the business activity even before the GDP data is released. If PMIs are below forecasts or 50, this means that the economy needs stimulation and may lead to a round of cutting rates by the Federal Reserve;
- Trade balance. The deficit in the trade balance is one of the biggest threats to the US dollar. Therefore, if the balance is negative, this may lead to further US dollar depreciation.
Political Instability
The US dollar is a global reserve currency, which is always used by traders and investors as a haven asset. In times of political instability, market participants buy the US dollar, while when the situation is rather stable, traders and investors prefer risky assets.
How to Predict the DXY Price Fluctuations: Technical Analysis
Apart from fundamental analysis, traders can use various technical analysis tools to predict price fluctuations. Similar to other assets, you can use technical indicators, chart patterns, Japanese candlestick analysis, Fibonacci, and others to predict price fluctuations.
Using Technical Indicators to Analyze the DXY Index
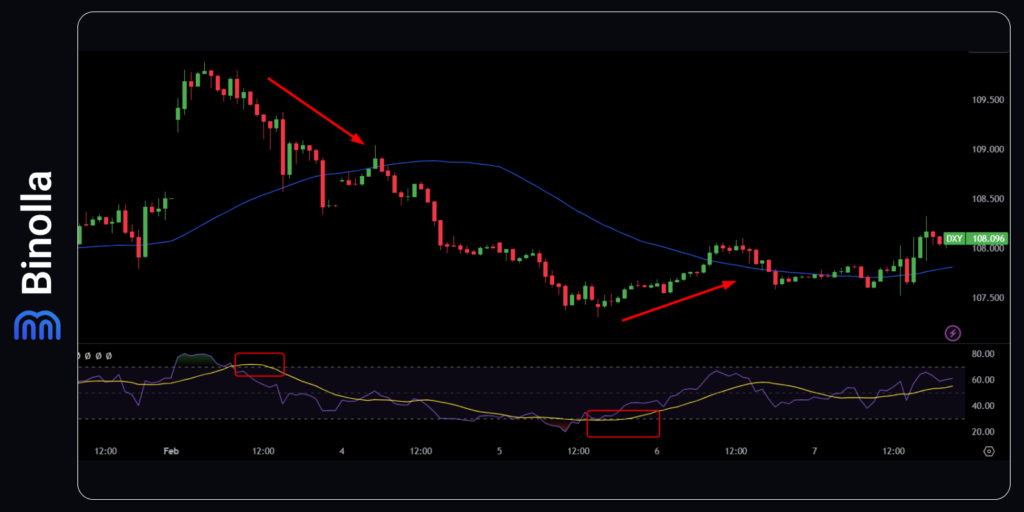
The Relative Strength Index is one of the most popular technical indicators so far, offering quite a simple and straightforward user interface. The tool allows traders to see when the price is overbought and oversold and find entry points when the US dollar index is going to reverse or at least have a correction.
Forex
When the price leaves the overbought area (above 70), a trader can sell the DXY index, while when it leaves the oversold area (below 30), the index is likely to increase, and a trader can buy the asset.
Digital Options
Digital options traders can buy a Lower contract when the indicator goes below 70 from the overbought area. If the RSI is below 30 and then moves above this level, traders buy a Higher contract.
Trading The DXY Index with Chart Patterns
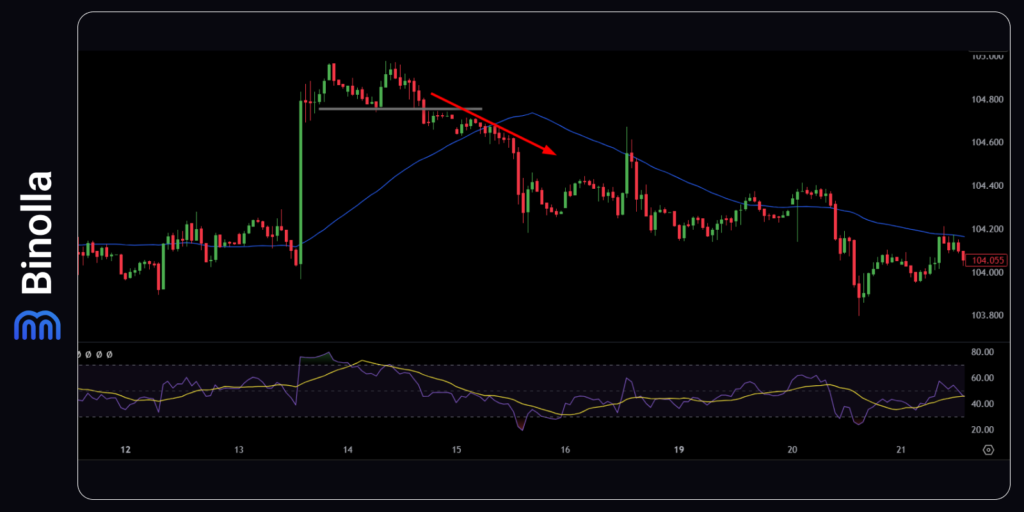
Traders can analyze DXY price fluctuations using various chart patterns. In this particular example, there is a double top pattern that normally appears right before the downside reversal.
Forex
To trade the double top pattern, you need to wait until the price breaks the support level, which is also known as the neckline. Once this happens, a trader sells the asset.
Digital Options
Those who use digital options can buy a Lower contract when the price breaks below the neckline. A trade should be placed right at this moment as the trader will make money on the momentum that comes right away.
Candlestick Reversal Patterns
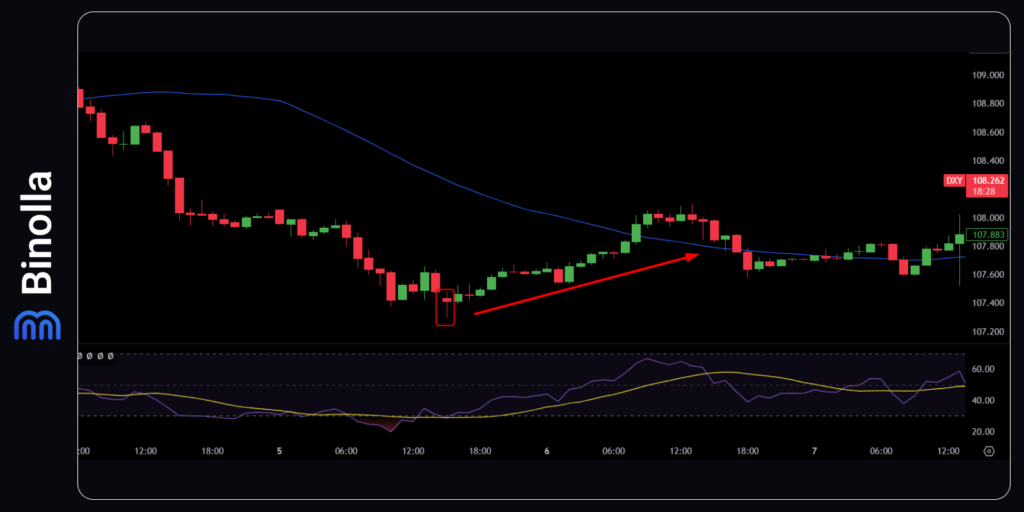
Using candlestick reversal patterns is another approach that will allow you to try to predict price fluctuations. A standard hammer, for instance, will tell you that the market is likely to make an upside reversal in the near future, while a shooting star may predict a downside reversal.
Forex
CFD traders can buy the DXY index after the next candlestick following the hammer pattern breaks above the hammer’s highest point. Stop losses can be placed right below the hammer’s low.
Digital Options
The hammer pattern can be traded by digital option traders as well. It is recommended to buy a Higher contract at the moment when the price breaks above the hammer’s highest point.
Conclusion
The DXY index is an opportunity for a trader to get exposure to one of the most popular and liquid currencies in the world of financial markets. Apart from simply trading it, the index allows market participants to analyze the general dollar trend and use this information when trading other assets. Traders can use a variety of tools to try to predict future price fluctuations of the US dollar index, including fundamental analysis, technical indicators, chart patterns, etc.
FAQ

What is the Difference Between the DXY and USD?
The US dollar index represents the value of the US dollar based on its relations to six major currencies.
What Does the US Dollar Index Tell Market Participants?
It allows traders and investors to see the current health and performance of the US dollar compared to other currencies.
What Are the Most Common Names and abbreviations of the US Dollar Index?
The most popular names and abbreviations of the US dollar index include DXY, USDX, DX, or “Dixie”.
Can I Buy and Sell the DXY Index?
Yes, you can. The index was traded as a futures contract originally, but nowadays, it is also available in the form of a contract for difference.







