Developing a Trading Plan: Setting Goals and Objectives

In the realm of business, there’s an age-old saying: “Fail to plan, plan to fail.” While it might sound cliche, those who are earnest about achieving success, traders included, should treat these words as gospel. Speak to any consistently profitable trader, and they’ll likely attest that your path boils down to two choices: rigorously adhere to a meticulously crafted trading plan or face failure.
If you find yourself armed with a written trading or investment plan, consider yourself part of a select group. Crafting such a plan demands time, dedication, and thorough research to develop a methodology that resonates within the financial markets. While success is never guaranteed, the act of formulating a comprehensive trading plan eradicates a significant obstacle on your journey. Whatever financial instrument you choose, digital options, Forex CFDs, stocks, or even cryptocurrencies, having a well-developed plan may change everything for the better.
So, if you’re already in possession of a well-detailed trading plan, kudos to you. You’ve bypassed a crucial hurdle that many overlook. However, for those still in the process or contemplating embarking on this journey, remember that success in trading, much like any endeavor, demands meticulous planning, discipline, and a commitment to your strategy. By reading this article, you will discover more about the basics of the trading plan as well as about features that you can include in it. If you are ready to trade already, then you can create an account at Binolla.
Contents
Trading Plan Basics
A trading plan serves as a comprehensive blueprint that outlines a trader’s approach to the financial markets. At its core, it encapsulates the trader’s goals, strategies, risk management protocols, and execution tactics. Think of it as a roadmap that guides the trader through the complexities of trading, providing clarity, structure, and discipline in their decision-making process.
The foundation of a trading plan lies in clearly defined objectives. Traders must identify what they aim to achieve through their trading activities, whether it’s capital preservation, consistent profitability, or portfolio growth. These objectives serve as the guiding principles that inform every aspect of the trading plan, from strategy selection to risk management.
Speaking of strategies, a trading plan articulates the methodologies and techniques that the trader will employ to identify trading opportunities and execute trades. These strategies could range from trend following and momentum trading to mean reversion and breakout trading, depending on the trader’s preferences, risk appetite, and market analysis.
Equally important is the integration of robust risk management protocols into the trading plan. Risk management is the bedrock of successful trading, as it aims to protect capital and mitigate potential losses. Traders must determine their position sizing, set stop-loss orders, and adhere to risk-reward ratios to ensure prudent risk management practices.
Furthermore, a trading plan fosters disciplined decision-making and emotional control. By establishing specific rules and guidelines for entering and exiting trades, the plan minimizes the influence of impulsive or irrational behavior. This discipline is crucial for maintaining consistency and resilience in the face of market volatility and uncertainty.
A trading plan is a dynamic document that evolves with the trader’s experience, market conditions, and objectives. It requires regular review, evaluation, and adjustment to ensure its alignment with the trader’s evolving needs and goals. Whether novice or seasoned, every trader can benefit from the creation and implementation of a well-crafted trading plan, as it provides the structure, clarity, and discipline necessary for navigating the complexities of financial markets.
A Ready-Made Trading Plan Template

To create your first trading plan, you can use the points that are described below. However, to make it even easier for you, we propose a template that you can use in your first trading sessions. You can adjust every single point here according to your own trading system.
An Intraday Trading Plan Template for Beginners (Digital Options)
| Trading objectives | Generate consistent profit from your everyday trading sessions |
| Goals | Achieve a trading profit target of [amount] Limit daily losses to [amount]Reach an average monthly return of [amount] |
| Trading strategy | The trading strategy is based on [patterns, indicators]Buying a Higher contract once a hammer, bullish engulfing, a morning star, or other reversal pattern appears on the support line or ascending trendlineBuying a Lower contract when a shooting star, hanging man, bearish engulfing, evening star or other reversal patterns appear on the resistance level or descending trendlineCheck the asset’s daily average volatility and the number of pips the asset covers within 24 hours |
| Market Context | Avoid trading on strong fundamentals, and check key fundamentals on a daily/weekly basis (for those who do not use news trading strategies) Use the key fundamentals, including labor market, inflation, and GDP data, and watch for central banks’ meetings or minutes to find entry points (for those who apply news trading strategies) |
| Confirmation | Utilize confluence of signals to confirm reversals |
| Assets | Forex currency pairs (EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/CAD) |
| Risk Management | Position sizing: a trading position should not exceed [percentage] of the deposit amount. Review the size of a trade after the previous contract is closed. Do not open more than [number] trades per day, week, month |
| Timeframes | From 1 minute to 1 hour. 1-minute, and 5-minute timeframes can be used for making decisions while 1-hour timeframe is good to overview the current local trends. |
| Trading Sessions | Trading will be conducted during [Sydney, Tokyo, London, New York] trading session |
| Review and Adjustment | Review the results of each trade, analyze the winners and losersAdjust a strategy after reviewing the latest trading resultsKeep recording the outcomes in a trading journal |
| Emotions | Avoid emotional tradingStick to the trading plan and strategyWait for high-probability patterns and signals, exercise patience |
A Trading Plan Template for Beginners (Forex CFD)
| Trading objectives | Generate consistent profit from your everyday trading sessions |
| Goals | Achieve a trading profit target of [amount] Limit daily losses to [amount]Reach an average monthly return of [amount] |
| Trading strategy | The trading strategy is based on [patterns, indicators]Buying a currency pair/stock/cryptocurrency when a bullish reversal pattern appears. These can be hammer, engulfing, morning star, etc. Buy when the price moves along the ascending trendlineBuying an asset (FX currency pair, stock, cryptocurrency) when a shooting star, hanging man, bearish engulfing, evening star or other reversal patterns appear on the resistance level or descending trendlineCheck the asset’s daily average volatility and the number of pips the asset covers within 24 hoursDon’t buy at a distance of [amount] pips from the resistance level. Don’t sell at a distance of [amount] from the support level |
| Market Context | Avoid trading on strong fundamentals, and check key fundamentals on a daily/weekly basis (for those who do not use news trading strategies) Use the key fundamentals, including labor market, inflation, and GDP data, and watch for central banks’ meetings or minutes to find entry points (for those who apply news trading strategies) Watch for spreads during data releases. Don’t buy or sell if the spread exceeds [amount of pips] Watch for swaps when leaving a trade active for more than one day |
| Confirmation | Utilize confluence of signals to confirm reversals |
| Assets | Forex currency pairs, stocks, cryptocurrencies |
| Risk Management | Position sizing: a trading position should not exceed [percentage] of the deposit amount. Review the size of a trade after the previous contract is closed Risks: stop losses should not exceed [amount of pips] for each trade Move the stop loss at the breakeven level once the price moves at [number of pips] in the forecasted direction Profit: take profit orders should be [number of pips] from the order price Reward-to-risk ratio: the reward-to-risk ratio is [2:1, 3:1, or other] Do not open more than [number] trades per day, week, or month in order to avoid overtrading |
| Timeframes | From 1 minute to 1 hour. 1-minute, and 5-minute timeframes can be used for making decisions while 1-hour timeframe is good to overview the current local trends (for intraday or short-term trading) A Daily timeframe can be used for mid-term trading strategies with a weekly timeframe to see major trends A weekly timeframe can be used for long-term trading strategies with a monthly timeframe to check major trends |
| Trading Sessions | Trading will be conducted during [Sydney, Tokyo, London, New York] trading session |
| Review and Adjustment | Review the results of each trade, analyze the winners and losersAdjust a strategy after reviewing the latest trading resultsCheck your stop losses and take profit orders to adjust them if necessaryKeep recording the outcomes in a trading journal |
| Emotions | Avoid emotional tradingStick to the trading plan and strategyWait for high-probability patterns and signals, exercise patience |
What Is a Trading Journal and How to Use It?
A trading journal serves as a valuable tool for traders to track and analyze their trading activities systematically. It acts as a comprehensive record of all trades executed, capturing crucial details such as entry and exit points, trade duration, position size, and reasons for trade decisions. By meticulously documenting each trade, traders gain insights into their trading behavior, patterns, and performance over time.
In addition to trade-specific information, a trading journal also allows traders to record their thoughts, emotions, and observations before, during, and after each trade. This qualitative data provides valuable context and helps traders understand the psychological factors influencing their decision-making process. By reflecting on their emotions and mental states, traders can identify patterns of behavior that may impact their trading performance and develop strategies to manage them effectively.
Moreover, a trading journal facilitates continuous improvement and learning by enabling traders to review and analyze past trades objectively. By identifying strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement, traders can refine their trading strategies, optimize risk management techniques, and enhance their overall performance. Ultimately, a trading journal empowers traders to make more informed decisions, cultivate discipline and consistency, and progress towards their trading goals with greater confidence and proficiency.
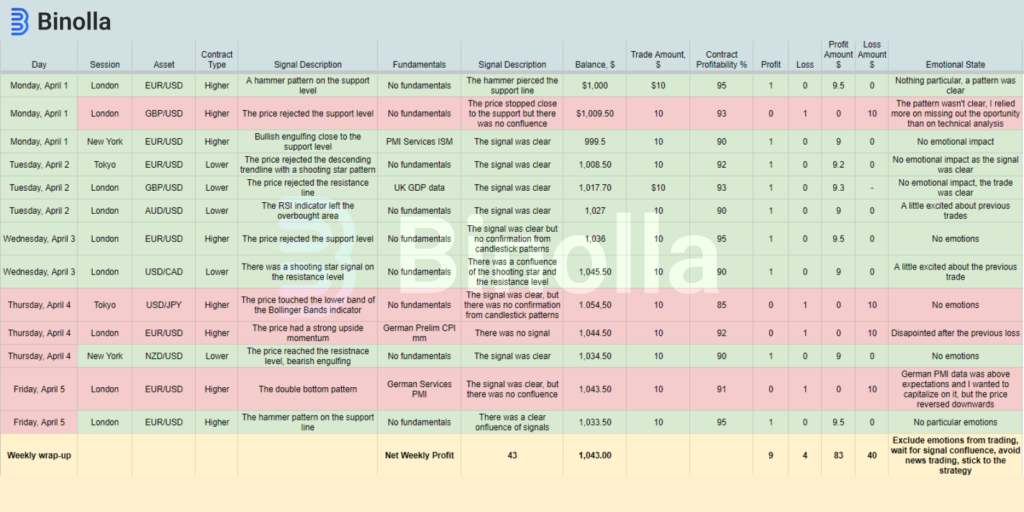
We have prepared an example of a trading journal from a beginner trader with all the trades as well as the emotional state described. You don’t need to follow this exact example, but you can use it as a template for your own trading journal.
How to Build a Trading Plan: What Aspects Should Be Considered
Two trading plans will never look the same. They may have similar structures that include some key parameters like setting the goals or a strategy that is used by a trader, but when delving deeper, you will see that the filing is always different. While we can’t give you a ready-made trading plan that you can use from scratch, we can provide you with some points that you can add or even build your trading plan around.
Setting Your Trading Goals
Setting trading goals is a critical aspect of developing a successful trading plan and achieving long-term success in the financial markets. These goals serve as the foundation upon which traders build their strategies, guiding their actions and decisions in pursuit of specific outcomes. Here’s why setting trading goals is essential and how to do it effectively. Trading goals should be set regardless of the financial instrument you use. They are relevant for digital options, Forex, stocks, commodities, and cryptocurrencies.
Firstly, trading goals provide traders with a sense of direction and purpose. By clearly defining what they aim to achieve through their trading activities, whether it’s capital preservation, consistent profitability, or portfolio growth, traders can align their actions with their objectives. This clarity helps traders stay focused and motivated, even during challenging market conditions.
Moreover, trading goals act as benchmarks for measuring progress and evaluating performance. By setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals, traders can track their progress over time and identify areas for improvement. Whether it’s achieving a certain percentage return on investment, increasing trading consistency, or reducing drawdowns, these goals provide tangible targets for assessing success.
When setting trading goals, it’s essential to consider factors such as risk tolerance, time horizon, and market conditions. Traders should assess their risk appetite and determine the level of risk they are willing to accept in pursuit of their goals. Additionally, they should consider their time horizon and whether they are trading for short-term gains or long-term growth. Lastly, traders should adapt their goals to prevailing market conditions, adjusting their strategies accordingly to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks.
Furthermore, trading goals should be realistic and achievable. While it’s important to aim high and challenge oneself, setting unrealistic goals can lead to frustration and disappointment. Traders should set goals that are ambitious yet attainable, taking into account their level of experience, resources, and market conditions. Additionally, traders should break down larger goals into smaller, manageable milestones to maintain momentum and stay motivated.
Setting trading goals is a fundamental step in developing a successful trading plan and achieving consistent profitability in the financial markets. By providing direction, motivation, and a framework for assessing progress, trading goals empower traders to navigate the complexities of trading with confidence and discipline. Whether novice or seasoned, every trader can benefit from setting clear, achievable goals that align with their objectives and aspirations.
Choosing A Trading Style

Selecting a trading style is a crucial decision for any trader, as it determines the approach they will take to the markets and influences their overall trading strategy. There are various trading styles, each with its own characteristics, advantages, and challenges. Here’s what traders should consider when selecting a trading style.
Firstly, traders should assess their personal preferences, risk tolerance, and lifestyle factors. Different trading styles require varying levels of time commitment, capital, and emotional resilience. Day trading, for example, involves executing multiple trades within a single day and requires quick decision-making and discipline. Swing trading, on the other hand, involves holding positions for several days or weeks, allowing for more flexibility and less time pressure. Traders should choose a style that aligns with their personality, schedule, and financial goals. If a trader uses digital options as their primary financial instrument, then choosing a trading style becomes easier as long-term and mid-term strategies are not applied for such contracts.
Secondly, traders should consider their level of experience and skillset. Certain trading styles may be better suited for beginners, while others may require more advanced knowledge and expertise. Scalping, for instance, involves making rapid-fire trades to capitalize on small price movements and requires a high level of precision and execution speed. Position trading, on the other hand, involves taking longer-term positions based on fundamental analysis and may be more suitable for experienced traders with a deep understanding of market dynamics.
Additionally, traders should assess market conditions and trends when selecting a trading style. Certain styles may perform better in specific market environments. For example, momentum traders may thrive in trending markets with strong price momentum, while range traders may excel in sideways or choppy markets. By adapting their trading style to prevailing market conditions, traders can maximize their chances of success and minimize risks.
Furthermore, traders should test and refine their chosen trading style through backtesting and demo trading. This allows them to evaluate the effectiveness of their strategy, identify strengths and weaknesses, and make necessary adjustments before committing real capital. Traders should be open to experimentation and continuously seek to improve their skills and performance over time.
Selecting a trading style is a significant decision that requires careful consideration of various factors, including personal preferences, experience, market conditions, and risk tolerance. By choosing a style that aligns with their goals and abilities, traders can develop a consistent and sustainable trading strategy that maximizes their chances of success in the financial markets.
Picking a Particular Class of Asset
Choosing a particular type of asset is a pivotal step in creating a proper trading plan, as it fundamentally shapes the trading strategy, risk management approach, and overall success in the financial markets. Different types of assets, such as stocks, Forex, commodities, or cryptocurrencies, exhibit unique characteristics and behaviors that require tailored trading plans to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks effectively. Here’s why selecting the right asset is crucial for crafting a proper trading plan:
Each type of asset class has distinct market dynamics and factors driving price movements. For example, stocks are influenced by company fundamentals, earnings reports, and broader market sentiment, while Forex is driven by economic indicators, central bank policies, and geopolitical events. Commodities are sensitive to supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical tensions, and weather conditions, while cryptocurrencies are influenced by technological developments, regulatory changes, and investor sentiment. By choosing an asset class that aligns with their knowledge, expertise, and interests, traders can develop a deeper understanding of the market and make more informed trading decisions.
Different types of assets offer varying levels of liquidity, volatility, and trading hours, which can impact trading strategy and execution. For instance, Forex markets are highly liquid and operate 24 hours a day, allowing for flexible trading opportunities and tight spreads. Stocks, on the other hand, may have lower liquidity and limited trading hours, requiring traders to be more selective in their trade timing and execution. Commodities may exhibit periods of high volatility due to supply disruptions or geopolitical events, while cryptocurrencies are known for their extreme price fluctuations and round-the-clock trading. By understanding the unique characteristics of each asset class, traders can tailor their trading plans to capitalize on opportunities and manage risks effectively.
The choice of asset class influences the risk-return profile of the trading plan and determines the appropriate risk management strategy. Different assets carry varying levels of risk and return potential, depending on factors such as volatility, leverage, and market conditions. Traders should assess their risk tolerance, investment objectives, and capital allocation preferences when selecting an asset class for their trading plan. For example, conservative investors may prefer trading forex pairs with lower volatility and tighter spreads, while more aggressive traders may seek higher returns through trading volatile stocks or cryptocurrencies. By aligning the risk-return profile of the chosen asset class with their trading goals and risk management strategy, traders can optimize their chances of success and achieve their financial objectives.
Choosing a particular type of asset is a critical decision that significantly impacts the effectiveness and success of a trading plan. By selecting an asset class that aligns with their knowledge, expertise, and risk preferences, traders can develop a tailored trading strategy, execute trades with confidence, and achieve their financial goals in the dynamic and competitive world of financial markets.
Trading Strategy Development
It is impossible to create a good and reliable trading plan without developing a good strategy. Trading strategy development is a systematic process that involves designing, testing, and refining a set of rules and guidelines to guide trading decisions in the financial markets. A well-developed trading strategy is essential for achieving consistent profitability and managing risk effectively. Here’s an overview of the key steps involved in trading strategy development:
- Market Analysis. The first step in developing a trading strategy is to conduct a thorough market analysis. This involves studying historical price data, identifying patterns and trends, and analyzing market dynamics. Traders may use technical analysis tools, such as chart patterns, indicators, and oscillators, as well as fundamental analysis factors, such as economic indicators, news events, and geopolitical developments, to inform their trading decisions.
- Strategy Formulation. Based on market analysis, traders formulate a trading strategy that outlines specific entry and exit criteria, risk management parameters, and position sizing rules. The strategy should be tailored to the trader’s objectives, risk tolerance, and trading style. For example, a trend-following strategy may involve entering trades when a security’s price breaks above or below a moving average, while a mean reversion strategy may involve trading reversals at key support or resistance levels.
- Backtesting. Once a trading strategy is formulated, traders conduct backtesting to evaluate its performance over historical data. Backtesting involves applying the strategy’s rules to past market conditions to assess its profitability, win rate, drawdowns, and other performance metrics. Traders use backtesting software or spreadsheet tools to simulate trades and analyze the results. This helps traders identify strengths and weaknesses in the strategy and make necessary adjustments.
- Optimization. After backtesting, traders may optimize their trading strategy to improve its performance. This may involve tweaking parameters, such as moving average lengths, indicator settings, or entry/exit rules, to enhance profitability or reduce risk. However, traders should be cautious not to over-optimize their strategy, as this can lead to curve-fitting and reduced robustness in real-market conditions.
- Risk Management. Risk management is a crucial aspect of trading strategy development. Traders must define their risk tolerance, set stop loss orders, and implement position-sizing rules to protect capital and minimize losses. Risk management should be integrated into the trading strategy to ensure consistency and discipline in risk-taking behavior.
- Demo Trading. Before deploying a trading strategy with real capital, traders should test it in a simulated trading environment using a demo account. Demo trading allows traders to practice executing trades, assess the strategy’s performance in real-time market conditions, and gain confidence in its effectiveness.
- Live Trading. Once a trading strategy has been thoroughly tested and refined, traders can deploy it in live trading with real capital. It’s essential to start with small position sizes and gradually increase exposure as confidence in the strategy grows. Traders should continue to monitor and evaluate the strategy’s performance in live trading and make adjustments as needed.
Some Basic Strategies that You Can Add to Your Trading Plan
If you haven’t developed any strategy yet, then the next part of the article will be useful to you. By reading it, you will find a couple of interesting tactics that can be added to your trading plan.
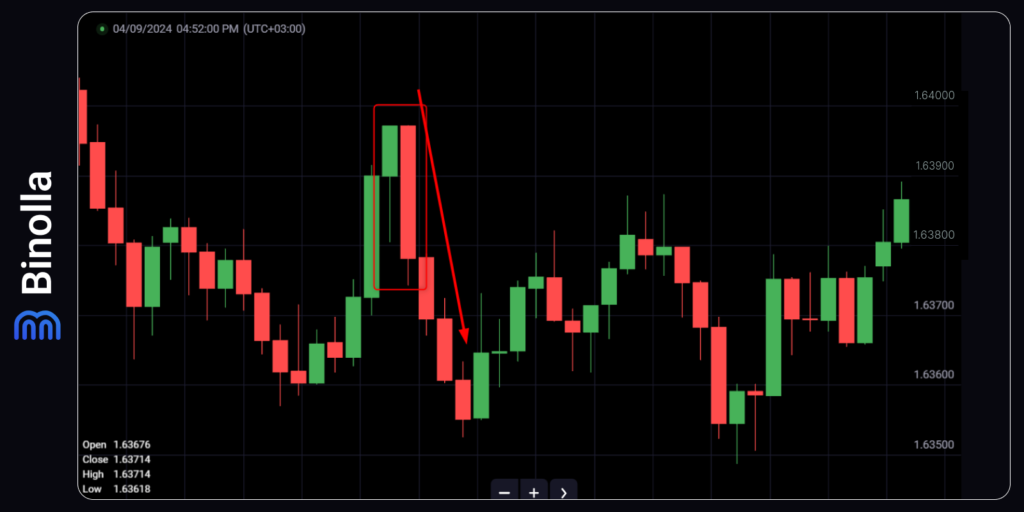
The first simple strategy involves Japanese candlestick patterns. There is a bearish engulfing on the chart, which is a signal for a trader to buy a Lower contract or to sell a currency pair/stock.
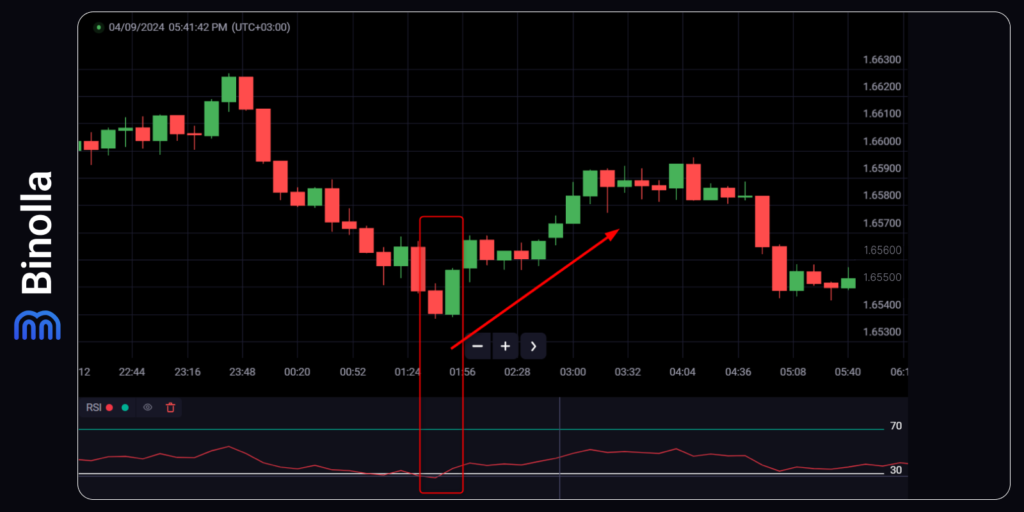
Another basic strategy uses a confluence of signals. We have a bullish engulfing here, which is a buy signal, and the RSI line lives the oversold area (breaks the 30 horizontal level), which is another buy signal. Therefore, when using such a strategy, traders can buy Higher contracts or go long when they trade Forex or stocks.
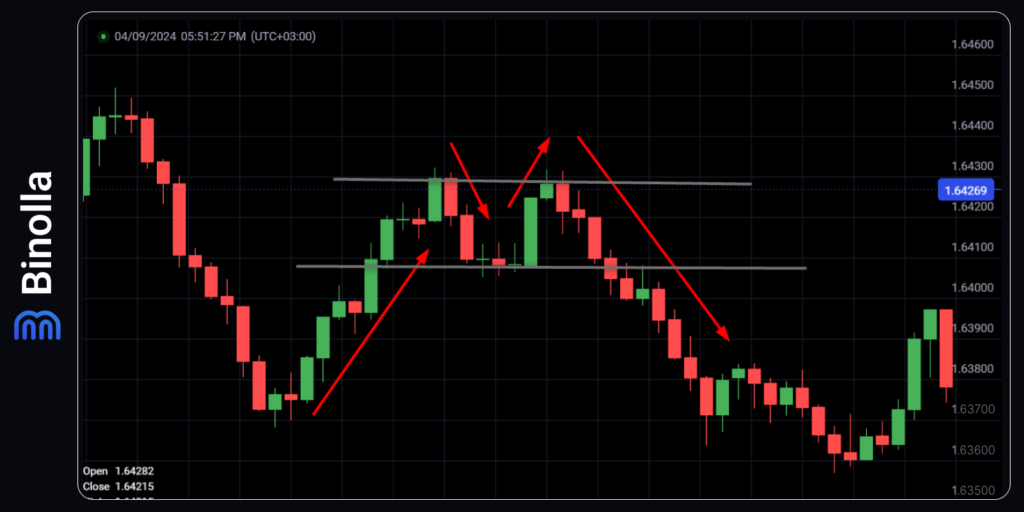
In the next strategy, we use the pattern known as double top to find the entry point. Here, when you see two price peaks at the same level, you can prepare for trading. Once the price breaks the support level, you can buy a Lower contract or go short.
Risk Management Rules
Risk management is a fundamental aspect of any trading plan, playing a crucial role in preserving capital, minimizing losses, and ensuring long-term success in the financial markets. Rather than viewing risk as an obstacle, traders should approach it as a manageable factor that can be mitigated through effective risk management rules integrated into their trading plan. Keep in mind that risk management rules are designed mostly for Forex, stock, and cryptocurrency traders. Those who use digital options as their primary financial instrument will have their risks protected by the nature of the contract as you can’t lose more than you have invested in a single contract.
One of the primary risk management rules is position sizing, which involves determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to each trade. By limiting the size of each position relative to the total trading capital, traders can mitigate the impact of potential losses on their overall portfolio. This ensures that no single trade has the potential to significantly erode the account balance, thereby protecting against catastrophic drawdowns.
Another key aspect of risk management is the use of stop-loss orders. These orders act as a safety net, allowing traders to exit losing trades before they escalate into larger losses. By setting predefined stop-loss levels based on technical analysis, support/resistance levels, or volatility, traders can limit their downside risk while allowing for potential upside gains. Stop-loss orders help enforce discipline and prevent emotional decision-making in the heat of market fluctuations.
Additionally, assessing the risk-reward ratio before entering a trade is essential for evaluating the potential profitability and risk exposure of the trade. Traders should aim for a favorable risk-reward ratio, where the potential reward outweighs the potential risk. By targeting trades with a higher reward-to-risk ratio, traders can ensure that the potential gains justify the potential losses, enhancing the overall profitability of their trading strategy.
Furthermore, diversification is a critical risk management strategy that involves spreading risk across multiple trades, asset classes, and markets. By diversifying the trading portfolio, traders can reduce correlation among trades and minimize the impact of individual trade losses on the overall portfolio. Diversification helps smooth out equity curve fluctuations and enhance risk-adjusted returns over time.
Lastly, risk management rules should be adaptable to changing market conditions and evolving trading strategies. Traders should continuously monitor their risk exposure, reassess their risk management rules, and make adjustments as needed. Flexibility and adaptability are essential traits for successful risk management in dynamic and unpredictable market environments.
In summary, incorporating robust risk management rules into a trading plan is essential for protecting capital and achieving long-term success in the financial markets. By integrating position sizing, stop-loss orders, risk-reward ratios, diversification, and adaptability into their trading plan, traders can effectively manage risk and navigate the complexities of trading with confidence and discipline.
Conclusion
Trading plans serve as indispensable roadmaps for traders navigating the complexities of the financial markets. By encompassing clear objectives, well-defined strategies, robust risk management protocols, and continuous evaluation, trading plans provide structure, discipline, and guidance for traders in their pursuit of consistent profitability and long-term success. Whether novice or seasoned, every trader can benefit from the clarity, consistency, and resilience that a well-crafted trading plan brings to their trading endeavors. In the ever-evolving landscape of trading, a solid trading plan remains an essential tool for achieving one’s financial goals and navigating the ups and downs of the market with confidence and discipline.
FAQ

What is a trading plan?
A trading plan is a comprehensive document that outlines a trader’s approach to the financial markets, including their goals, strategies, risk management rules, and execution tactics.
Why is a trading plan important?
A trading plan is important because it provides structure, discipline, and guidance for traders in their decision-making process. It helps traders stay focused on their objectives, manage risk effectively, and navigate the complexities of the market with confidence.
What elements should a trading plan include?
A trading plan should include clear objectives, defined strategies for entering and exiting trades, robust risk management protocols, and guidelines for evaluating performance. It should be adaptable to changing market conditions and reflect the trader’s unique goals, preferences, and trading style.
How often should a trading plan be reviewed and updated?
A trading plan should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure its alignment with the trader’s evolving goals, market conditions, and trading performance. Traders should conduct periodic evaluations to assess the effectiveness of their strategies, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments to their plans accordingly.