Bitcoin Reached Its ATH Over $70,000: How to Trade the First Cryptocurrency

Bitcoin or BTC traded less than ¢1 in 2010 and made impressive growth over the years. The first cryptocurrency reached $74,000 in 2024 and, according to forecasts, this is not the end of the rally. Some experts predict BTC to hit $200,000 and even higher. Other crypto enthusiasts expect the cryptocurrency to surpass $600,000 and even hit $1,000,000.
With all the above, BTC attracts a lot of attention and many traders want to trade this digital asset. Whether you are a digital options trader or a market participant trading Forex or stocks, cryptocurrencies may attract your attention. Open the account at Binolla to enjoy digital options trading right now. By reading this article, you will find out more about the key factors that influence Bitcoin price and discover some basic technical analysis strategies that you can use when buying or selling BTC. If you are looking for more information on how to trade cryptocurrencies, you can explore this article.
Start trading at Binolla and discover our variety of financial assets.
Contents
- 1 Bitcoin Basics
- 2 The Key Factors that Affect Bitcoin’s Price
- 3 Give crypto trading a try with Binolla!
- 4 Key Bitcoin Price Milestones
- 5 Bitcoin Trading Strategies
- 6 Tips to Trade Bitcoin
- 7 The Advantages and Disadvantages of Bitcoin Trading
- 8 FAQ
Bitcoin Basics
Before delving deeper into aspects that every trader should know about Bitcoin trading, it is worth looking into the basics of the first cryptocurrency.
BTC, the pioneer cryptocurrency, operates on a decentralized peer-to-peer network known as the blockchain. At its core, Bitcoin’s technical side revolves around cryptographic principles, distributed consensus mechanisms, and innovative protocols that enable secure and transparent transactions.
One of the key technical features of Bitcoin is its blockchain, a public ledger that records all transactions ever made on the network. Each block on the blockchain contains a list of transactions, and these blocks are linked together in chronological order, forming a continuous chain. This decentralized nature of the blockchain ensures transparency and immutability, as transactions cannot be altered or tampered with once they are confirmed and added to the blockchain.
Underpinning the security of the Bitcoin network is its consensus mechanism, known as Proof of Work (PoW). PoW requires network participants, known as miners, to solve complex mathematical puzzles in order to validate transactions and create new blocks. Miners compete to solve these puzzles, with the first one to find a valid solution earning the right to add the next block to the blockchain. This process not only validates transactions but also ensures the integrity of the network by making it computationally expensive to manipulate the blockchain.
Another crucial aspect of Bitcoin’s technical architecture is its cryptographic algorithms. Bitcoin uses cryptographic hash functions, such as SHA-256, to secure transactions and create digital signatures. These algorithms ensure that each transaction is authenticated and cannot be forged or altered. Additionally, public-key cryptography is employed to generate unique addresses for users, enabling them to send and receive bitcoins securely.
Bitcoin transactions are broadcasted to the network and then included in blocks by miners. Each one includes inputs, which are references to previous transactions that provide the Bitcoins being spent, and outputs, which specify the recipients of the bitcoins. Transactions must be digitally signed by the sender using their private key to prove ownership of the bitcoins being transferred.
To maintain a stable money supply and control inflation, Bitcoin has a predetermined issuance schedule. The total supply of bitcoins is capped at 21 million, and new bitcoins are issued to miners as block rewards for successfully adding blocks to the blockchain. However, the block reward is halved approximately every four years in a process known as “halving,” which gradually reduces the rate of new Bitcoin creation until the maximum supply is reached.
The Key Factors that Affect Bitcoin’s Price

Now that you know more about the technical part of the project, it is time to delve into the key fundamentals that may have a significant impact on the BTC’s price.
Bitcoin’s price is subject to a multitude of factors, ranging from market sentiment and investor behavior to macroeconomic trends and regulatory developments. Understanding these key factors is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the volatile world of cryptocurrency trading and investment. Here, we delve into the primary influencers that shape Bitcoin’s price dynamics.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
Bitcoin’s limited supply of 21 million coins is a fundamental factor driving its price. As demand for Bitcoin increases, driven by factors such as institutional adoption, retail investment, and global economic uncertainty, its scarcity becomes more apparent, leading to upward price pressure. Conversely, a decrease in demand relative to supply may result in price corrections.
The Bitcoin halving event, occurring approximately every four years, exerts a significant influence on the cryptocurrency’s price dynamics. Fundamentally, the halving is a mechanism embedded within the Bitcoin protocol aimed at regulating the issuance rate of new bitcoins. This reduction in the rate of new supply issuance directly impacts Bitcoin’s supply and demand dynamics.
Following each halving event, the rate at which new bitcoins are mined is slashed by half. This reduction translates into a decrease in the available supply of bitcoins entering the market. With a finite maximum supply of 21 million bitcoins, the halving underscores Bitcoin’s scarcity. Scarcity, being a fundamental driver of value, tends to result in upward price pressure on Bitcoin.
Historical data indicates that previous halving events have been accompanied by significant price rallies in Bitcoin’s price. Both the 2012 and 2016 halving events were heralded by periods of accumulation and followed by substantial bull markets. These rallies are often attributed to a combination of reduced selling pressure from miners due to decreased block rewards and heightened demand from investors expecting future scarcity.
Furthermore, the halving event can evoke psychological responses among market participants, influencing investor sentiment and speculative behavior. Anticipation of reduced future supply and potential price appreciation may lead to increased buying pressure and speculative demand in the lead-up to the halving event. Media coverage, social media discussions, and public awareness surrounding the halving event can contribute to hype and FOMO (fear of missing out) among retail investors, further fueling buying pressure.
Miner economics also plays a crucial role in the halving’s impact on Bitcoin’s price. The halving directly affects the profitability of Bitcoin mining operations, as miners receive fewer bitcoins for each block they mine. Consequently, miners may need to adjust their operations or upgrade equipment to remain profitable. Some miners may choose to sell a portion of their Bitcoin holdings to cover operational expenses, leading to short-term selling pressure. However, the reduction in selling pressure from miners over time, combined with increased demand from investors, can contribute to long-term price appreciation following the halving event.
The Bitcoin halving event serves as a fundamental mechanism for controlling the issuance rate of new bitcoins and maintaining the cryptocurrency’s scarcity. While the halving event alone may not guarantee price appreciation, its influence on supply and demand dynamics, historical price trends, market psychology, and miner economics collectively contribute to significant price movements in Bitcoin’s price both before and after each halving event.
Market Sentiment and Investor Psychology

Market sentiment, driven by factors such as news events, social media discussions, and investor sentiment indicators, can have a profound impact on Bitcoin’s price movements. Positive news, such as institutional adoption or regulatory approvals, often leads to bullish sentiment and price appreciation, while negative news, such as security breaches or regulatory crackdowns, can trigger sell-offs and price declines.
Investor psychology, including fear, greed, and herd behavior, also plays a critical role in shaping Bitcoin’s price. Fear-driven sell-offs during market downturns and FOMO (fear of missing out) induced buying frenzies during bull runs are common examples of how investor emotions can drive short-term price volatility.
Adoption and Acceptance
The Increasing adoption and acceptance of Bitcoin as a legitimate store of value and medium of exchange contribute to its long-term price appreciation. Institutional adoption by corporations, investment funds, and payment processors, as well as growing acceptance by merchants and consumers worldwide, validate Bitcoin’s utility and drive demand.
Regulatory clarity and institutional infrastructure, including regulated cryptocurrency exchanges, custodial services, and investment vehicles such as Bitcoin ETFs (exchange-traded funds), play a crucial role in facilitating broader adoption and attracting institutional capital into the Bitcoin market.
Technological Developments
Technological advancements and innovations within the Bitcoin ecosystem, such as improvements in scalability, privacy, and security, can impact its price dynamics. Upgrades to the Bitcoin protocol, such as the implementation of the Lightning Network for faster and cheaper transactions, or advancements in cryptographic privacy solutions, may enhance Bitcoin’s utility and attractiveness to users and investors.
Conversely, vulnerabilities or technical challenges within the Bitcoin network, such as network congestion, high transaction fees, or security breaches, may undermine confidence and lead to short-term price volatility.
Macro-Economic Factors

Bitcoin’s price is influenced by broader macroeconomic trends, including monetary policy, inflation, and geopolitical developments. Economic instability, currency devaluation, or concerns about central bank policies, such as quantitative easing or negative interest rates, may drive demand for Bitcoin as a hedge against fiat currency depreciation and inflation.
Additionally, geopolitical tensions, trade wars, and global economic uncertainty can trigger risk-off sentiment in traditional financial markets, leading investors to seek alternative assets such as Bitcoin and gold as safe-haven investments, thereby influencing Bitcoin’s price positively.
The decisions made by the Federal Reserve (the Fed), the central banking system of the United States, have a significant impact on financial markets worldwide, including the price of Bitcoin. The Fed’s monetary policy decisions, interest rate changes, and quantitative easing (QE) programs can influence investor sentiment, market volatility, and the value of fiat currencies, all of which can indirectly affect the price of Bitcoin in various ways.
Interest Rate Decisions
The Fed’s decisions regarding interest rates can have a direct impact on Bitcoin’s price. When the Fed raises interest rates, it typically strengthens the U.S. dollar relative to other currencies, making it more attractive for investors to hold dollars and reducing the appeal of alternative assets like Bitcoin.
Conversely, when the Fed lowers interest rates or maintains an accommodative monetary policy stance, it can lead to a weakening of the dollar and increased inflationary pressures. In such cases, investors may seek alternative stores of value, including Bitcoin, as a hedge against currency depreciation and inflation, potentially driving up its price.
Quantitative Easing (QE) Programs
The Fed’s implementation of QE programs, which involve the purchase of government bonds and other securities to inject liquidity into the financial system, can impact Bitcoin’s price dynamics. QE programs typically lead to an expansion of the money supply and lower interest rates, which can fuel inflationary pressures and weaken the purchasing power of fiat currencies.
In response to QE measures and concerns about currency debasement, investors may allocate a portion of their portfolios to alternative assets like Bitcoin, which is perceived as a scarce and deflationary asset immune to central bank manipulation. This increased demand for Bitcoin as a hedge against inflation can drive up its price.
Market Sentiment and Risk Appetite
The Fed’s statements, speeches by policymakers, and economic data releases can influence investor sentiment and risk appetite, which in turn can impact Bitcoin’s price. Positive economic indicators or indications of robust growth may boost risk appetite and confidence in traditional financial markets, leading investors to allocate funds to riskier assets like Bitcoin.
Conversely, negative economic news, concerns about recessionary pressures, or uncertainties surrounding Fed policy decisions may trigger risk aversion and flight to safety, prompting investors to seek refuge in less volatile assets such as cash or government bonds, potentially dampening demand for Bitcoin.
Inflation Expectations
The Fed’s inflation target and its ability to maintain price stability are closely monitored by market participants. Changes in inflation expectations, as reflected in the Fed’s statements or inflation data releases, can impact Bitcoin’s price dynamics.
Inflationary pressures or expectations of future inflation may increase the appeal of Bitcoin as a hedge against fiat currency devaluation and inflationary risks. As a decentralized digital asset with a fixed supply cap, Bitcoin is often viewed as a store of value and a hedge against inflation similar to gold.
Market Liquidity and Trading Activity
Liquidity, trading volume, and market depth in Bitcoin markets play a crucial role in determining its price stability and susceptibility to manipulation. High liquidity and trading activity on major cryptocurrency exchanges contributes to smoother price discovery and reduced price volatility.
However, low liquidity and thin order books on smaller exchanges or illiquid trading pairs may increase the risk of price manipulation by whales or large traders, leading to sudden price spikes or crashes.
Sleeping Wallets and Whales
“Sleeping wallets” and “whales” are two terms commonly used in the context of cryptocurrency markets, particularly Bitcoin, and they can have notable effects on its price dynamics.
Sleeping wallets refer to cryptocurrency wallets that have been inactive for an extended period, often holding significant amounts of Bitcoin. These wallets belong to early adopters, miners, or investors who may have acquired Bitcoin in the early stages of its existence and have since chosen to hold onto it for the long term.
When Bitcoin from sleeping wallets enters the market, it can impact supply dynamics. If a large number of dormant Bitcoins suddenly become active and are sold, it can lead to increased selling pressure, potentially causing downward price movements. Conversely, if holders of sleeping wallets choose not to sell their Bitcoin, it can contribute to a reduction in available supply, which may lead to upward price pressure, especially in times of high demand.
In the cryptocurrency world, a “whale” refers to an individual or entity that holds a significant amount of Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies. Whales often have the capacity to influence market prices due to the size of their holdings and their ability to execute large trades.
The actions of whales, such as buying or selling large quantities of Bitcoin, can have a substantial impact on price movements. For example, if a whale decides to sell a significant portion of their Bitcoin holdings, it can trigger a sell-off in the market, leading to price declines. Conversely, if a whale purchases a substantial amount of Bitcoin, it can create buying pressure and drive prices higher.
Additionally, whales may engage in market manipulation tactics, such as “pump and dump” schemes, where they artificially inflate the price of Bitcoin through coordinated buying and then sell off their holdings at a profit once prices have risen significantly. Such activities can contribute to short-term price volatility and may negatively affect smaller investors.
Both sleeping wallets and whales play significant roles in shaping Bitcoin’s price dynamics. While sleeping wallets represent long-term holders whose actions may reflect broader market sentiment and supply dynamics, whales have the potential to influence prices through their large trades and market manipulation tactics. Traders and investors in the Bitcoin market often monitor the activities of both sleeping wallets and whales to gauge potential price movements and make informed trading decisions.
Regulatory Environment
Regulatory developments and government interventions in the cryptocurrency space can have a significant impact on Bitcoin’s price. Regulatory clarity, favorable regulations, and government support for blockchain innovation and cryptocurrency adoption may boost investor confidence and drive price appreciation.
Conversely, regulatory crackdowns, bans, or restrictive measures imposed by governments or regulatory authorities can create uncertainty and negative sentiment, leading to price declines and market turmoil.
Key Bitcoin Price Milestones
2013: Bitcoin Makes an Impressive 6,000%+ Growth
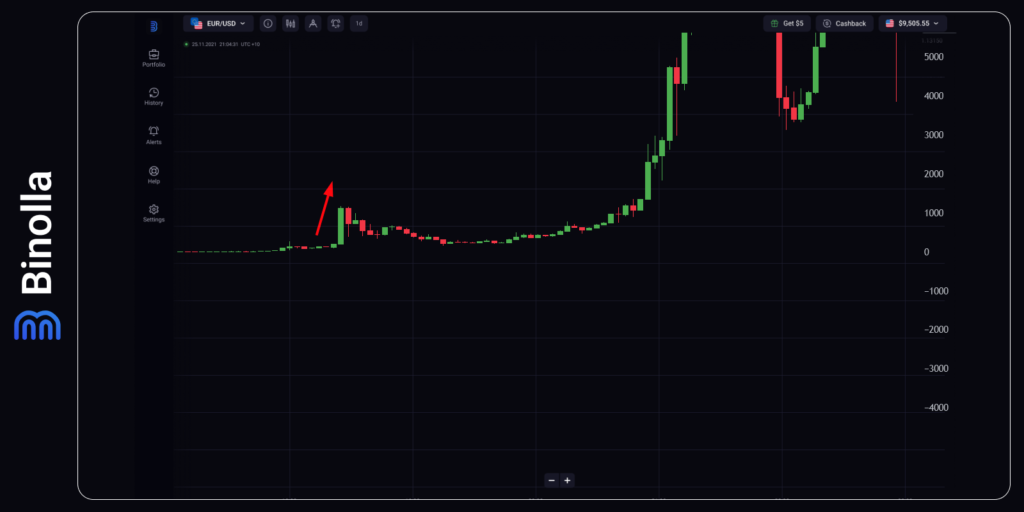
Several reasons fueled Bitcoin’s price in 2013. First, it should be mentioned that the first halving of the cryptocurrency that cut the miners’ reward from 50 to 25 BTC, took place on November 28, 2012. This was a so-called “past-halving” reaction that provided unprecedented support to the coin and triggered its skyrocketing growth. This supply and demand dynamics factor will influence Bitcoin’s price several times in the future.
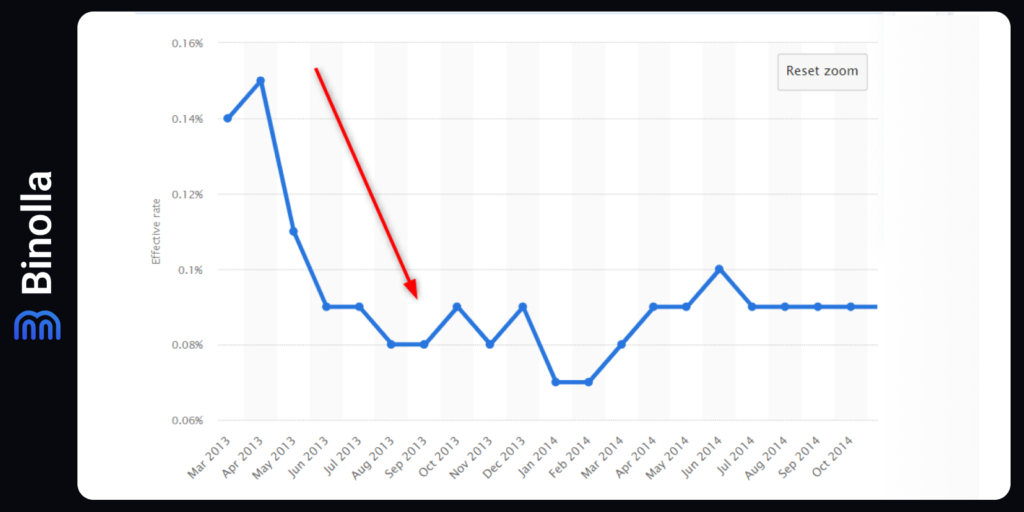
Second, The Fed’s rates fell below 0.1% in this period. Together with the unprecedented QE that was launched in 2012 by Ben Bernanke, this factor played a significant role in BTC’s massive growth during that period. A lot of cheap liquidity flooded the markets and part of it reached Bitcoin.
Another factor that supported the very first cryptocurrency was the number of upgrades and developments that were made in the blockchain ecosystem during this period. Moreover, the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) resumed accepting Bitcoin, bolstering its legitimacy and fueling investor confidence. In addition, the installation of the world’s inaugural Bitcoin ATM in Vancouver revolutionized access to cryptocurrencies, allowing individuals to convert cash into digital assets seamlessly. Adoption and acceptance play a very important role.
What Happened in the Market?
Bitcoin experienced remarkable growth, starting the year at $13 and soaring to a peak of almost $1,100. This surge marked a historic milestone, with the cryptocurrency witnessing an unprecedented gain of 6,600% – a testament to its meteoric rise in popularity and value.
Despite reaching dizzying heights, Bitcoin endured substantial volatility, witnessing a sharp correction of over 50% in April. However, it rebounded resiliently, consolidating for six months before embarking on another historic rally towards the end of the year.
This bullish momentum propelled Bitcoin’s market capitalization beyond the $1 billion mark for the first time, underscoring its growing influence in the financial landscape. Nevertheless, the journey was not devoid of challenges, as Bitcoin’s price plummeted by 85% from its peak, testing investors’ resilience.
Amidst the fervent market activity, emerging cryptocurrencies like Dogecoin garnered attention, showcasing the burgeoning interest in digital assets. Despite its origins as a meme coin, Dogecoin persisted and remains a notable presence in the cryptocurrency space.
The events of 2013 exemplify the remarkable volatility and resilience of Bitcoin, laying the groundwork for its enduring significance in the financial world.
The First Great Bitcoin Rally in 2017
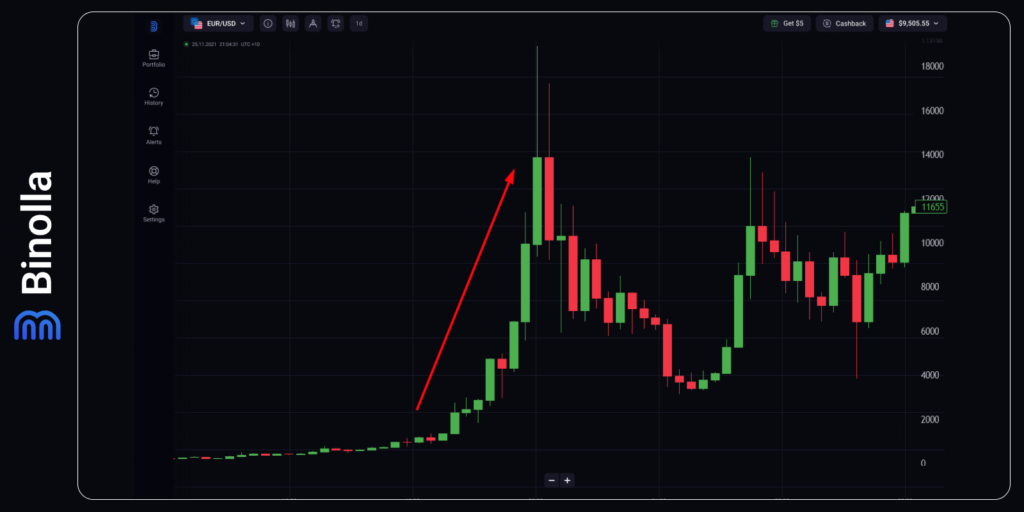
The next halving took place on July 9, 2016. The reward for the block was cut from 25 to 12,5 Bitcoins, which was one of the reasons for the first cryptocurrency to make another impressive growth in 2017. This time, the monetary policy in the US was not among the reasons but could have an additional impact as rates remained at their lowest levels.
The Fed started to hike rates in 2016 and by 2017, they were between 0.75% and 1%. However, further monetary policy tightening was among the reasons for the following downturn, that happened in 2018 and 2019.
There was a counter-driver that led to a volume drop that year. The People’s Bank of China decided to tighten crypto regulation and three major cryptocurrencies that operated in the country, closed their fiat trading activities, which, in turn, resulted in less cash inflow to the blockchain industry.
Another negative driver that restrained Bitcoin price growth was the rejection of the first ETF by the SEC. It is worth mentioning that the Winklevoss twins were pioneers in the attempt to legalize the first Bitcoin-based exchange-traded fund, but their initiative failed right in 2017.
How the Market Reacted to These Events?
In January 2017, Bitcoin surged past the $1,100 mark, marking a new all-time high. By December of the same year, the price skyrocketed to nearly $20,000, representing an astonishing 20-fold increase within a mere 12 months. However, this meteoric rise was followed by a subsequent downturn throughout 2018 and 2019, with Bitcoin struggling to regain momentum until late 2020.
During this period, opinions on Bitcoin varied widely, ranging from skepticism labeling it a scam to fervent belief in its revolutionary potential. For those who embraced the latter view, it presented an opportunity to explore and learn about investing in Bitcoin for the first time. However, the surge in retail interest also brought about heightened volatility across the cryptocurrency markets, underscoring the significant impact of retail investors on market dynamics.
Bitcoin Price Surge After a Long Crypto Winter in 2021
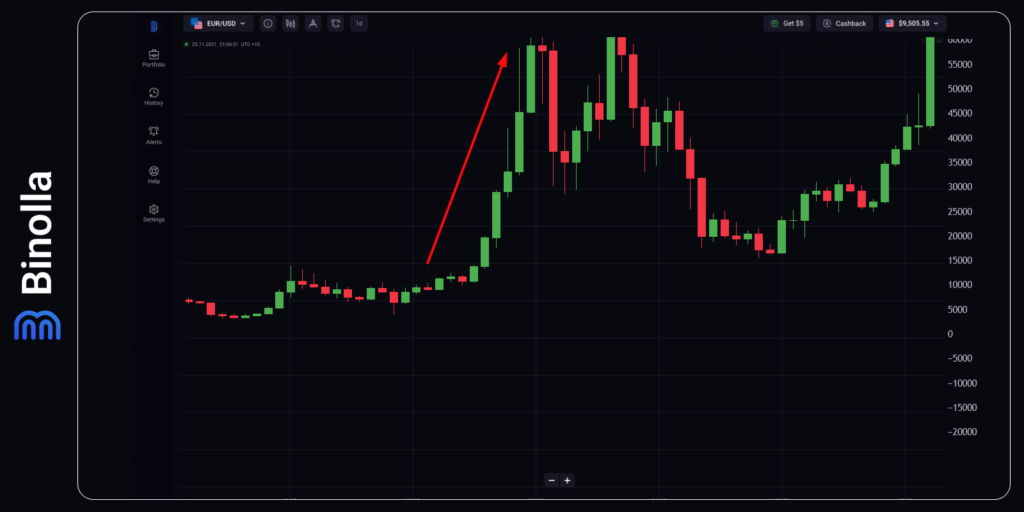
The next Bitcoin halving event took place in May 2020. However, the price remained in a narrow range until 2021, when the Fed decided to cut rates abruptly following the COVID restrictions to provide unprecedented support to the US economy during the pandemic. The Fed was quick to ease the monetary policy from 1.5% to 0% in a matter of one month, which unleashed unprecedented volumes of liquidity in the markets.
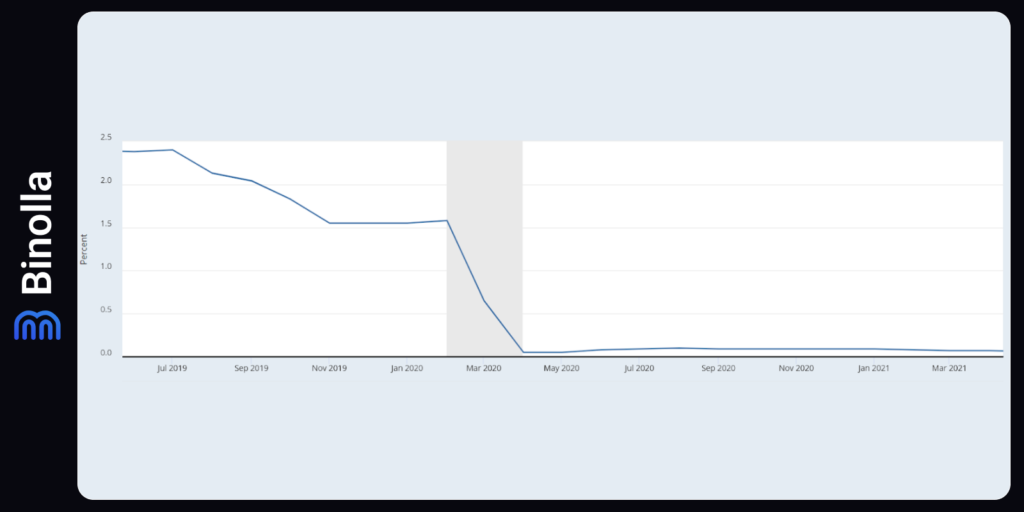
The coincidence of both macroeconomic and technical factors was among the main reasons for Bitcoin’s skyrocketing growth, which resulted in the price to overpass $65,000. Market sentiment is also worth adding to this basket as both key players and retail traders and investors were looking for an opportunity to store their wealth in a reliable asset. Despite its volatile nature and even lack of mass adoption, BTC played the role of both a safe haven and an asset with great growth expectations.

Elon Musk’s Dogecoin tweets are among significant drivers as well. The famous visionary and engineer supported the meme coin, which, in turn, impacted the whole crypto market. Moreover, earlier in 2021, Tesla, MicroStrategy, and Square started investing in BTC and other coins.
Speaking about fundamental reasons, El Salvador passed the law that made Bitcoin a legal payment method. The country was the first to make such a huge leap towards cryptocurrency adoption.
Last but not least, Bitcoin-based futures ETFs were launched in 2021, which was another gigantic step towards mass adoption of the first cryptocurrency and other blockchain-based coins and tokens.
How Bitcoin Reacted to These Events
In August 2021, Bitcoin’s price lingered near the $46,000 mark, but by November of the same year, it surged to an unprecedented peak, surpassing $68,500.
By the end of 2021, the Bitcoin hash rate, a metric often linked to Bitcoin’s price movements, experienced a significant decline, dropping to approximately $47,000—a staggering 30% decrease from previous levels.
This decline in price was attributed in part to China’s directive for its citizens to cease Bitcoin mining activities, a move that impacted a substantial portion of the network’s mining nodes previously located in the country. Consequently, these mining operations had to be taken offline, leading to a reduction in mining capacity. Many analysts assert that this diminished mining capacity played a pivotal role in exerting downward pressure on the Bitcoin price.
Furthermore, apprehensions surrounding the regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies were heightened as politicians and regulators voiced concerns about potential legislative measures. These uncertainties contributed to the prevailing sentiment within the cryptocurrency community, commonly referred to as FUD (fear, uncertainty, doubt)—a term emblematic of the plethora of crypto jargon now prevalent in the industry.
Investors and Traders Make Bitcoin Strong Again in 2024
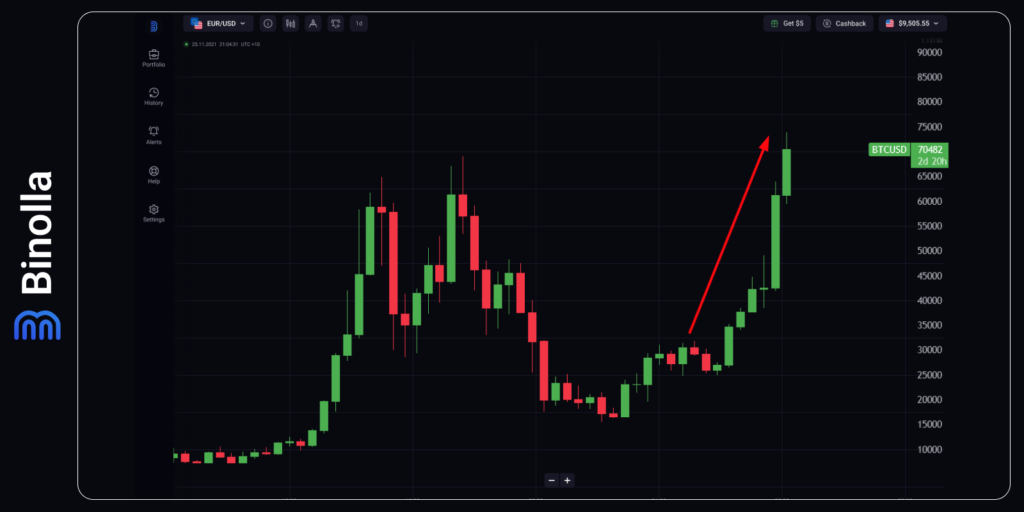
In anticipation of the next halving event that will take place on April 19, 2024, investors and traders increased their Bitcoin positions. Along with this some upgrades, including Taproot, improved the network efficiency, which, in turn, was another reason for market participants to pay attention to BTC.
However, not only technological factors contributed to this tremendous growth of the first cryptocurrency. The macroeconomic aspect played a huge role in this bull run as well. Traders and investors are waiting for the Fed to start cutting the rate in 2024. This move from the FOMC will ensure cheaper liquidity on the markets and, therefore, more market participants will join the rally.
The next important aspect that fueled this rally was the approval by the SEC of exchange-traded funds (ETFs). From now on, traders and investors can buy this basket of assets that track the BTC’s price. This event added a positive reputation and trust to the first cryptocurrency ever and made it even more attractive as by adapting Bitcoin ETFs, the SEC demonstrated the legality of BTC on behalf of one of the strictest financial regulatory bodies.
How Bitcoin Reacted to These Events
Starting from October 2023, Bitcoin soared again and the price of the first cryptocurrency made another ATH by almost hitting $74,000. This historical event and another milestone in the history of BTC’s price is due to a mixture of factors. First, we are on the eve of the next halving, which will reduce the miners’ rewards again.
Bitcoin Trading Strategies
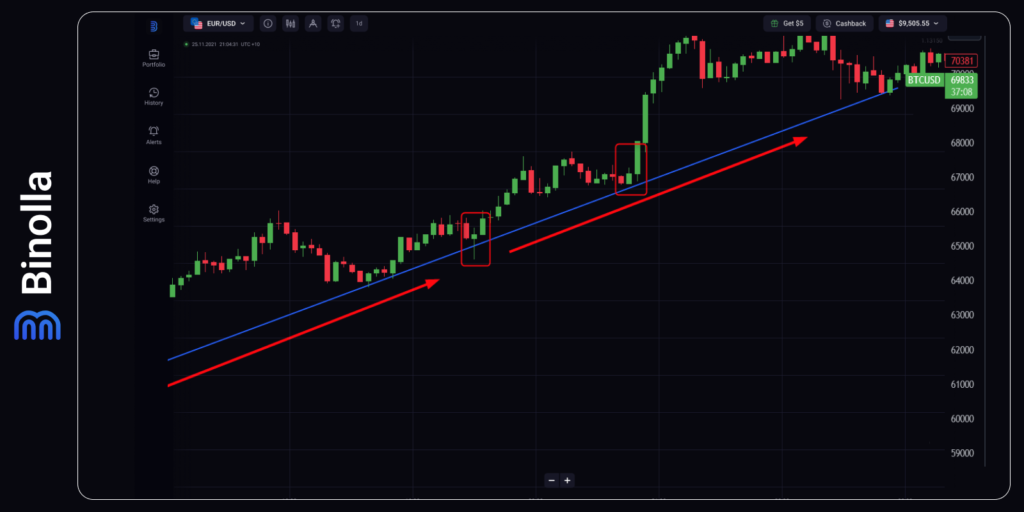
One of the basic strategies for cryptocurrency traders is swing trading. It is more suitable for FX traders as they can hold their positions longer and add to existing ones. However, even digital options traders can use it successfully.
First, to start using a swing trading strategy, you need to identify the current market trend. In the example above, we have an uptrend. Second, you should wait until the price retests the trendline after an upside movement. Once it happens, a market participant can start looking for a signal. In the first case, we have a hammer pattern that pierces the trendline. After the closure of the candlestick, a trader can buy a Higher contract or purchase Bitcoin.
The next signal comes further the trendline. The price returns to the ascending line again and a trader can buy a Higher contract or Bitcoin if they trade CFDs.
Trading Bitcoin on the Support Line
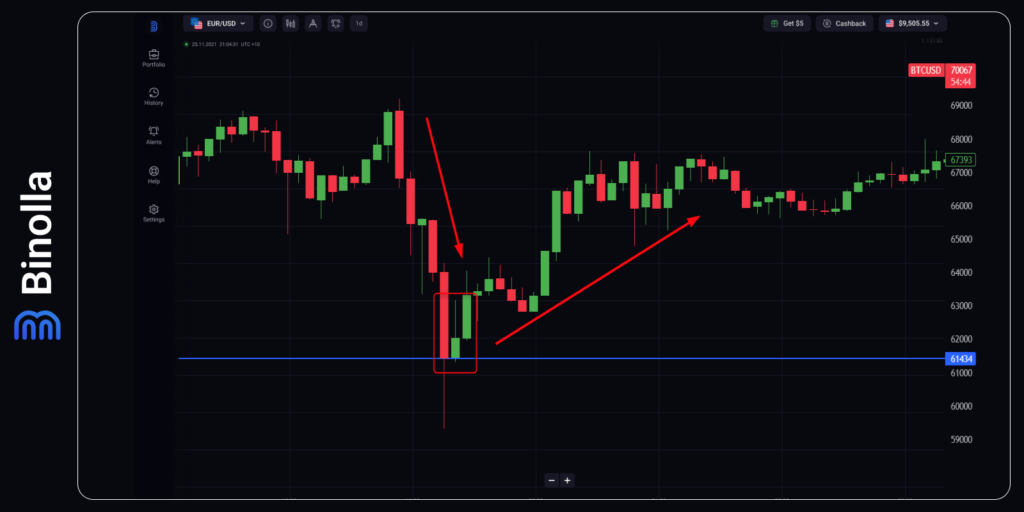
Another Bitcoin strategy that is worth your attention is when BTC goes down to the support line. Similar to the first signal from the previous strategy, here you can use a confluence of signals as the inverted hammer appears right on the level. The idea here is simple: buy a Higher contract or buy BTC once the inverted hammer candlestick is closed.
RSI Bitcoin Strategy
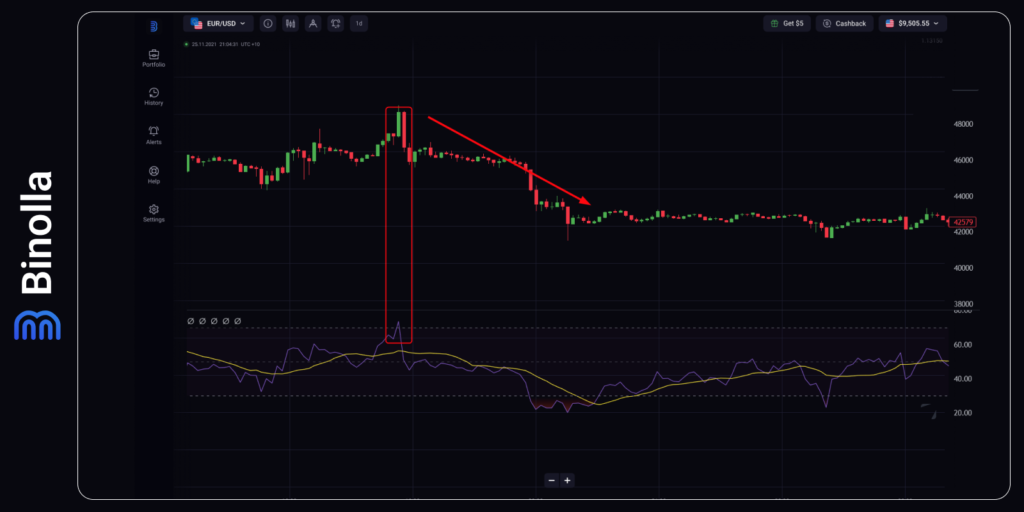
The next Bitcoin trading strategy that is worth mentioning is that with the RSI indicator. After you add the momentum technical analysis tool to the chart, you simply need to wait for the indicator to leave the overbought area. Once this happens, a trader can sell Bitcoin or buy a Lower contract. When using this strategy you should be aware of corrections. Digital options can apply this approach without limitations, but if you are looking for greater trends, you should add some more tools to make sure that you deal with a new trend instead of a retracement.
Double Moving Average Bitcoin Strategy
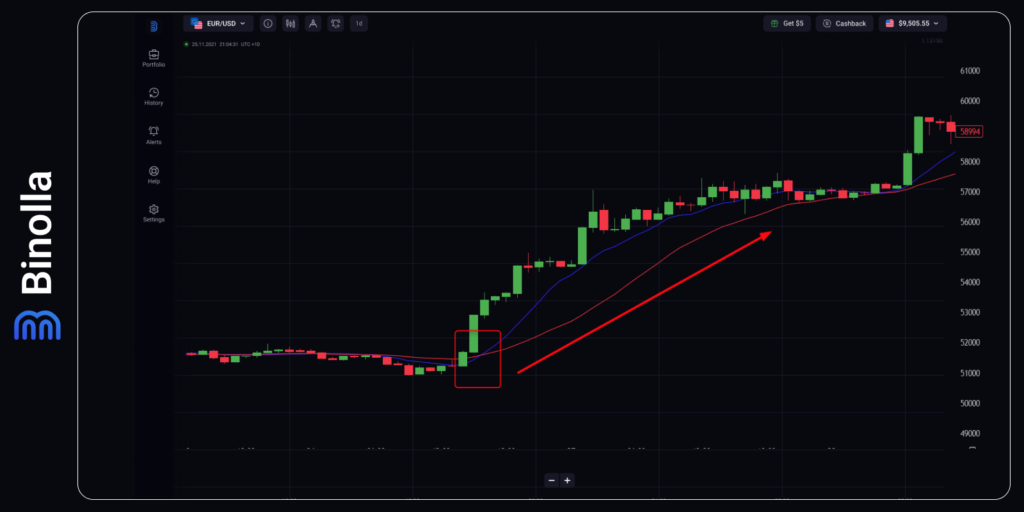
This simple Bitcoin trading strategy involves two moving averages with periods of 10 and 20. The signal comes when a shorter one crosses the longer one from below and starts moving above the latter. In the example above we can see that once this happens, a relatively long uptrend begins, which is a good opportunity for digital options traders to buy a Higher contract and for FX traders to purchase CFD on Bitcoin.
Tips to Trade Bitcoin
Trading Bitcoin can be both exciting and challenging due to its high volatility and unpredictable price movements. Whether you’re a novice trader or an experienced investor, here are some tips to help you navigate the world of Bitcoin trading more effectively:
- Educate Yourself. Before diving into Bitcoin trading, take the time to educate yourself about cryptocurrency markets, technical analysis, and trading strategies. Understanding key concepts such as support and resistance levels, candlestick patterns, and market indicators will help you make informed trading decisions;
- Start Small. Begin with a small investment and gradually increase your exposure as you gain experience and confidence in your trading strategy. Avoid investing more than you can afford to lose, especially in the highly volatile cryptocurrency markets;
- Set Clear Goals and Risk Management. Define your trading goals, whether it’s short-term profit-taking or long-term investment, and establish a clear risk management strategy. Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and adhere to your risk tolerance level to avoid emotional decision-making during periods of market volatility;
- Follow Market Trends. Keep abreast of market trends, news developments, and major events that may impact Bitcoin’s price. Follow reputable sources of information and analysis to stay informed about market sentiment and potential trading opportunities;
- Utilize Technical Analysis. Use technical analysis tools and charting software to analyze price trends, identify support and resistance levels, and spot potential entry and exit points. Common technical indicators such as moving averages, RSI (Relative Strength Index), and MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) can help you make more informed trading decisions;
- Diversify Your Portfolio. Consider diversifying your trading portfolio by allocating funds across multiple cryptocurrencies or trading pairs. Diversification can help spread risk and minimize the impact of adverse price movements in any single asset;
- Practice Patience and Discipline. Trading Bitcoin requires patience and discipline. Avoid chasing short-term price movements or succumbing to FOMO (fear of missing out). Stick to your trading strategy, remain disciplined in your approach, and avoid making impulsive decisions based on emotions;
- Stay Calm During Volatility. Bitcoin’s price can be highly volatile, with rapid price fluctuations occurring within short timeframes. During periods of heightened volatility, it’s essential to stay calm, avoid panic selling, and stick to your trading plan;
- Use Stop Loss Orders. Consider using stop-loss orders to automatically sell your Bitcoin holdings at predetermined price levels to limit potential losses. Stop loss orders can help protect your capital and mitigate risks during adverse market conditions. Keep in mind that this advice is not relevant for digital options traders;
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation. The cryptocurrency market is constantly evolving, so it’s essential to continue learning and adapting your trading strategy based on market conditions and new developments. Stay open-minded, be willing to experiment with different trading approaches, and always strive to improve your trading skills.
Remember that trading Bitcoin involves inherent risks, and there are no guarantees of profit. It’s crucial to conduct thorough research, exercise caution, and only invest what you can afford to lose. By following these tips and maintaining a disciplined approach to trading, you can increase your chances of success in the exciting world of Bitcoin trading.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Bitcoin Trading
There are plenty of benefits for those who decide to trade Bitcoin. Some of the key ones include:
- 24/7 Market. Unlike traditional stock markets, Bitcoin trades 24/7, allowing traders to take advantage of price movements at any time of the day, including weekends and holidays;
- Liquidity. Bitcoin markets are highly liquid, with significant trading volumes on various cryptocurrency exchanges worldwide. High liquidity reduces the risk of slippage and ensures that traders can easily enter and exit positions without significant price impact;
- Accessibility. Trading Bitcoin is accessible to anyone with an internet connection and a trading account. There are no barriers to entry, and traders can start with small amounts of capital;
- Potential for High Returns. Due to Bitcoin’s volatility, traders have the potential to earn high returns on their investments in a relatively short period. Successful traders can capitalize on price fluctuations to generate substantial profits.
Along with a lot of advantages, some drawbacks of trading Bitcoin are also should be considered:
- High Volatility. While Bitcoin’s volatility presents opportunities for profit, it also poses significant risks. Price swings can be extreme and unpredictable, leading to substantial losses for traders who fail to manage risk effectively;
- Market Manipulation. Cryptocurrency markets are susceptible to manipulation due to their relatively small size and lack of regulation. Whales (large holders of Bitcoin) can influence prices through coordinated buying or selling, leading to market distortions;
- Technical Complexity. Bitcoin trading requires a certain level of technical knowledge and expertise in areas such as chart analysis, order execution, and risk management. Novice traders may struggle to navigate the complexities of cryptocurrency trading and make informed decisions;
- Psychological Pressure. Trading Bitcoin can be emotionally taxing, especially during periods of heightened volatility or significant price swings. Fear, greed, and FOMO (fear of missing out) can cloud judgment and lead to impulsive or irrational trading decisions.
FAQ

What is Bitcoin trading?
Bitcoin trading involves the buying and selling of Bitcoin, the world’s first and most popular cryptocurrency, with the aim of making a profit from the price fluctuations in the market.
What trading strategies can I use for Bitcoin?
Common trading strategies for Bitcoin include day trading, swing trading, trend following, and scalping. Each strategy involves different timeframes, risk levels, and entry/exit points.
Is Bitcoin trading risky?
Yes, Bitcoin trading carries inherent risks due to the cryptocurrency’s high volatility and unpredictable price movements. Traders can potentially incur significant losses if they fail to manage risk effectively.
How can I manage risk in Bitcoin trading?
Risk management techniques in Bitcoin trading include setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, diversifying your trading portfolio, avoiding over-leveraging, and only trading with funds you can afford to lose.
What factors influence the price of Bitcoin?
Several factors influence Bitcoin’s price, including market sentiment, supply and demand dynamics, macroeconomic trends, regulatory developments, technological advancements, and geopolitical events.
Should I invest in Bitcoin or trade it?
Whether to invest in Bitcoin or trade it depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment strategy. Investing in Bitcoin involves buying and holding for the long term, while trading involves actively buying and selling to capitalize on short-term price movements.







