Bid and Ask Prices: How Spread Affects Trading and How to Mitigate Trading Costs

Bid and ask prices play a crucial role in trading as they allow market participants to set buy and sell orders correctly and better understand their trading costs. Moreover, by utilizing these types of prices, you will be able to improve your risk and money management techniques. By reading this article, traders will find out more about bid and ask prices, market spreads, and how to use them. We will provide some examples of how to calculate spreads and how they affect your trading results.
Ready to make your first trade? Join Binolla and enjoy the best trading conditions at the lowest costs!
Contents
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 Bid and Ask Prices Basics
- 3 Why Is It Important to Understand the Bid and Ask Prices in Trading?
- 4 Factors Affecting Spread
- 5 Example of Trading with Spread
- 6 Types of Spread in Trading
- 7 Trade with the Best Spreads with Binolla
- 8 Fixed vs. Floating Spreads: Which One is Better?
- 9 How to Mitigate Risks Related to Spread Costs
- 10 Conclusion
- 11 FAQ
Key Takeaways
- The bid price is the price at which a trader sells an asset;
- The ask price is the price at which a trader buys an asset;
- The spread is the difference between the bid and ask prices, which is the cost that a trader pays for each position;
- There are two types of spread – fixed and floating;
- A fixed spread is better for those who use scalping strategies and want to better plan their money and risk management strategies;
- Floating spreads should be chosen by traders who want to mitigate costs in times of lower volatility and higher liquidity.
Bid and Ask Prices Basics
Bid price refers to the price a buyer will pay to purchase an asset. The ask price is the price at which the seller sells the asset. To better understand the concept, it is worth mentioning that it is used by banks when you exchange currencies. You will always see two prices there: one is the price that you should pay for a currency, while another is the price at which the bank will buy a currency from you.
During the trading process, buyers and sellers seek to find the best bid and ask price. The difference between both prices is known as a spread. It can vary depending on the market situation and the perception of market makers.
If there is a reason to set the price higher, the seller can raise the ask price. Therefore, the buyer in this situation will also move the bid price higher, but still, it won’t reach the ask price. In situations when there is a reason to cut prices, the seller will push the ask price lower and the buyer will be ready to purchase an asset at a lower price.
When it comes to Forex brokers, they set both ask and bid prices on their own. The spread is a kind of commission that the brokerage company will earn once the deal is settled. By selling slightly above the market price, the broker will capitalize on this slight difference. On the other hand, the broker will also profit from buying an asset from a trader at a lower price.
Why Is It Important to Understand the Bid and Ask Prices in Trading?
The main reason for a trader to understand the bid and ask price is to see the size of the spread. When trading currency pairs, you will always buy and sell at worse conditions, which means that you will overpay a bit for a currency you buy and sell slightly below the market price.
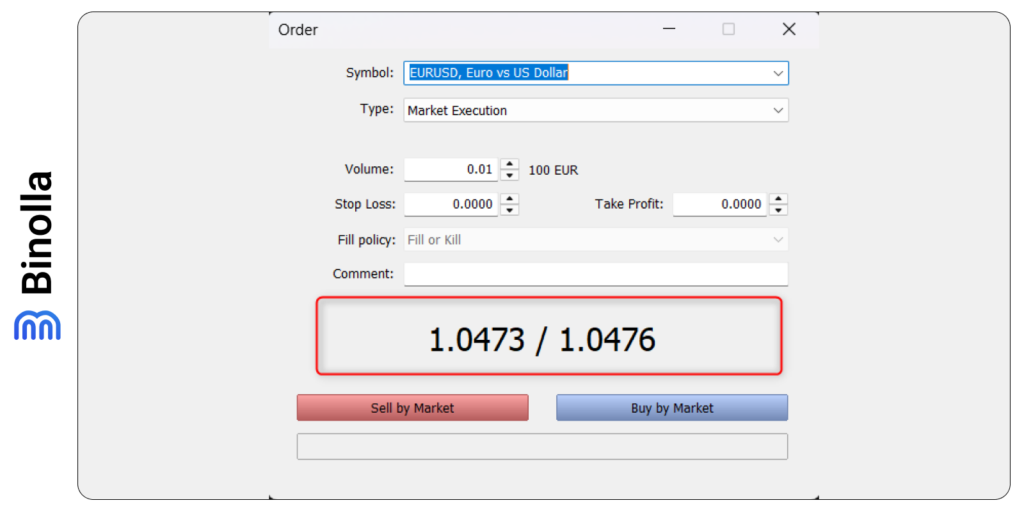
To see the spread, you can use the order window in the MetaTrader platform. Here you can see that the difference between the bid and ask prices is 0.0003, which means that for this particular currency pair the spread is 3 pips.
Factors Affecting Spread
As you already know, the spread is the difference between the bid and ask price. This value is not constant and it may be smaller or larger depending on several factors. Here are some of the most important ones:
- Market liquidity. Liquidity demonstrates how easily a trader or an investor can buy/sell an asset at a market price. Higher liquidity often leads to lower spreads as there is an abundance of bids and offers in the financial market. This reduces the difference between the bid and ask prices;
- Time. Spreads may be affected by the time. For instance, on Mondays during the Asian session, spreads may be higher due to the lower liquidity. On Fridays, before the market closure, spreads may increase as well;
- Fundamental factors. Major economic reports and officials’ comments can have a serious impact on spreads. They normally increase volatility and spreads as prices change quickly. Macroeconomic data and other important events can be watched in special economic calendars;
- Financial instruments. Spreads may vary depending on a particular financial instrument or currency pair. When it comes to Forex, currency pairs are famous for lower spreads than other types of assets. Moreover, even within Forex, there are currencies with lower and higher spreads;
- General market situation. Geopolitical events or instability may contribute to the spread increase.
Example of Trading with Spread
Now let’s see how a trade with a spread performed. Imagine that you are going to buy EUR/USD. The currency ask price is 1.0503, while the bid price is 1.0500. You purchase the currency pair at 1.0503. Keep in mind that once you open a trade, your loss will be 3 pips. If the bid price reaches 1.0503, then your profit will be 0 pips, and if the bid price moves higher, then your profit will grow.
The trick here is that if you want to make 10 pips, then you should wait until the price makes 13 pips. This is due to the fact that when closing the position, you will sell at bid price, which is three pips lower than the ask one. Therefore, if you decide to sell when the bid price is 1.0513 then the ask price will be 1.0510 and your profit will be seven pips instead of 10.
Types of Spread in Trading

There are two main types of spread in trading – fixed and floating. By choosing a particular one, a trader can benefit from unique market conditions and build their money and risk management strategies around them. Now let’s delve deeper into each type and see their benefits and drawbacks.
Fixed Spreads
As it comes from its name, this type of spread stays the same regardless of all the factors that may influence this parameter. Fixed spreads may differ depending on the asset you trade. For instance, for EUR/USD, the fixed spread may reach 3 pips, while for GBP/USD, this parameter may be 4 pips depending on the broker you choose. The key point here is that for EUR/USD the fixed spread will remain the same at any moment.
Fixed spreads are available when trading with a broker using a dealing desk model, which means that large positions are purchased via liquidity providers. Later, brokers offer those positions to traders in smaller sizes.
One of the biggest advantages of trading with fixed spreads is that you always know transaction costs. Therefore, you can plan your trading in advance. Moreover, traders can benefit from fixed spreads during times of higher volatility as the trading cost will remain the same. However, there are some important drawbacks that should also be considered.
First of all, those who choose fixed spread may face requotes, which is a change in price in fast-paced market conditions. Transaction will be blocked in this situation and you will be asked to accept the new price for the same trade.
Another drawback is slippage, which occurs in the same market situation. The broker can’t maintain the fixed spread when the price is rapidly changing and a trader pays a different amount of spread.
Floating Spreads
Unlike fixed spreads, floating ones change all the time depending on the bid and ask price difference. We have already pointed out the main reasons that affect spread fluctuations. They include liquidity, volatility, macroeconomic context, and others.
This type of spread is offered by companies that do not use the dealing desk mechanism. They receive prices from liquidity providers and offer them to market participants. Floating spreads offer their own benefits as traders won’t experience any requotes and slippages. However, some minor drawbacks still exist. Floating spreads may reach dozens of pips per asset especially in times of high volatility.
Fixed vs. Floating Spreads: Which One is Better?

Choosing between fixed and floating spreads may be difficult, especially for those who are new to trading. Both of them have advantages and disadvantages that you should consider before making the final choice.
| Pros | Cons | |
| Fixed Spreads | Fixed spreads are predictable and remain the same regardless of the current market situation. This allows you to know your trading costs in advance | Fixed spreads are normally larger as compared to floating ones, especially major currencies |
| When selecting fixed spreads, traders can avoid surprises when spreads may widen significantly in times of higher volatility | When trading with fixed spreads, you will have limited flexibility as in times of lower volatility, floating spreads may be more beneficial. This leads to higher costs as compared to floating spreads. | |
| Fixed spreads allow market participants to build various risk and money management strategies with a predictable outcome | ||
| Fixed spreads are ideal for scalpers as those using short-term strategies need to know their trading costs in advance to better manage them | ||
| Floating Spreads | Floating spreads offer more beneficial conditions for assets with higher liquidity as the difference between the bid and ask prices will be lower | Traders who use floating spreads can’t rely on predictability as such spreads change all the time |
| Better money and risk management in calm markets. When trading with floating spreads, you can expect better conditions when the volatility is low | Risks of higher spreads are among the strongest drawbacks of floating spreads. In times of higher volatility, you will have to pay more for a trade | |
| Floating spreads provide you with the highest level of flexibility as they change depending on the market situation. For instance, you can avoid trading in times of major economic releases and place trades during low-volatility periods | When it comes to scalping, floating spreads are not the best solution as they may increase significantly and eat up a significant part of your eventual profit |
Which Spread is Better?
Choosing between the fixed and floating spread is important and will be easier now that you know both the pros and cons of each type. You can choose the fixed one if you are looking for predictability in trading costs or if you are going to trade during volatile news releases or periods with lower liquidity. Fixed spreads are also the best solution for those using scalping strategies or for market participants who look for stable costs to better plan their money and risk management strategies.
When it comes to floating spreads, traders can choose them in times of higher liquidity when spreads are tighter and they are normally lower as compared to fixed spreads. Floating spreads are also better for market participants who can tolerate the occasional widening of spreads during periods of higher volatility.
How to Mitigate Risks Related to Spread Costs

Spreads are an integral part of trading and you can’t avoid them. However, market participants have several options allowing them to mitigate their influence on their trading results. Here are some key recommendations on how to improve the situation:
- Using limit orders. By placing Buy/Sell Stop/Limit orders market participants can set the level at which they are ready to buy or sell in advance and mitigate costs. In particular, a market participant can use a limit order to enter the market at a better price and with better spreads before important news is published;
- Choosing between assets. A trader should monitor the situation and select those assets with lower spreads that may go in the same direction. For instance, traders often choose major currency pairs as they boast higher liquidity as compared to minors;
- Choose brokers with lower average spreads. When analyzing a particular brokerage company, you should check the range of financial instruments and their spreads. Select the firm with the lowest possible average spreads and other commissions;
- Enter the market during peak hours. To mitigate costs related to spreads, traders can enter the market during so-called peak hours when the liquidity reaches its highest readings;
- Trade with higher volumes. Opening a position of higher size will help mitigate spread-related costs. This will also allow traders and investors to reduce spread costs over time;
- Select currency pairs with fixed spreads in times of higher volatility. Trading forex currencies with lower spreads in times of higher volatility will allow you to avoid situations when the spread is too high. However, you should always consider the risks of slippage and requotes;
- Do not trade during major news events. Some market participants avoid trading during major macroeconomic data releases and other events that may significantly increase volatility;
- Monitor the spread changes. To mitigate spread costs, traders should monitor spreads all the time and choose only those assets with the lowest difference between the bid and ask prices.
Conclusion
The bid and ask prices are very important for traders as they allow market participants to calculate spreads. The latter is the costs that you are going to pay for each trade. Knowing spreads will allow you to better manage your risks and create various strategies to mitigate trading costs. Choosing the brokerage company with lower spreads will allow you to increase your gains over time.
FAQ

What Does Spread Mean in Trading?
Spread is the difference between the bid and ask price, which stands for trading costs that every trader “pays” when opening a position.
What is the Difference Between the Bid and the Ask Price?
The bid price is the price at which you sell an asset in Forex, while the ask price is the price at which you buy an asset in the financial markets.
Which Spread is Better?
Tighter spreads are always better as your trading costs will be lower.
How to Calculate Spreads in Trading?
To do that, you need to deduct the bid price from the ask price. For example, for an asset with a bid price of 1.0300 and an ask price of 1.0305, the spread will be 5 pips.







